History of the United States
The United States is located in the middle of the North American continent, bordered by Canada to the north and Mexico to the south. The United States of America stretches from the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast to the Pacific Ocean on the west coast, including the Hawaiian archipelago in the Pacific Ocean, Alaska state on the northern tip of the Americas, and several other territories.
The first settler of the region that is now the United States came from Asia about 15,000 years ago. They cross the Bering land bridge to Alaska. [1] Furthermore, Native Americans settled in the area for thousands of years before the arrival of European colonists. In 1492, Christopher Columbus made it to America. The English then settled in Jamestown, Virginia in 1607. This settlement was considered the first settlement in the United States. Furthermore, the United States continues to be visited by the British people. The French, Spanish, and Dutch also settled in parts of the United States. [2] In the 1770s, thirteen British colonies included two and a half million inhabitants. These colonies grew and developed rapidly, and developed their own political and legal systems. Nonetheless, the development of the British colonies ended up bad for Native Americans, as many of them died from illness, and they lost their country.
The British parliament upholds its authority over these colonies by setting new taxes, which are considered unconstitutional by Americans because they are not represented in Parliament. [3] The heated conflict led to a full war that began in April 1775. After going through the American Revolution, the colonies declared independence from the Kingdom of Great Britain on July 4, 1776 and founded the United States.
With large-scale military and financial support from France and the leadership of General George Washington, the Patriot Forces won the Revolutionary War and peace was agreed in 1783. During and after the war, 13 nations united under the federal government established through the Confederate Articles. When this document ceased to work properly, the new Constitution was adopted in 1789 and up until then became the basis for the federal government of the United States, and later included the Human Rights Act. With Washington as its first president and Alexander Hamilton as its chief financial adviser, a strong national government was formed. In the First Party System, two national political parties grew up supporting or rejecting Hamilton's policies. When Thomas Jefferson became president, he bought the Louisiana Region from France, doubling the size of America. The second and final war against the United Kingdom took place in 1812. The main result of the war was the end of European support for Indian attacks on western settlers. 
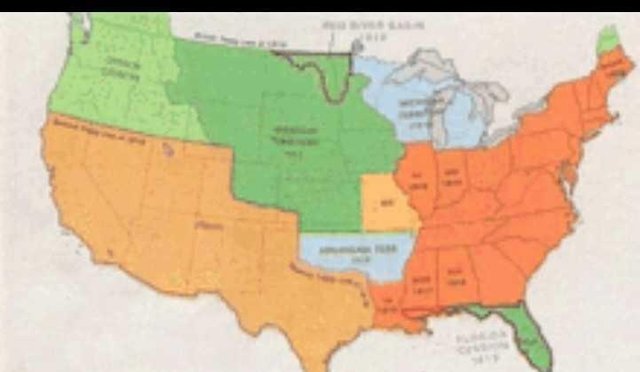
Under the support of Jefferson democracy and Jackson democracy, the United States extends through the purchase of Louisiana to the extent of California and Oregon, as well as the search for cheap land for the peasants and slaves of Yeoman who promote democracy and expansion, to be paid with violence and hatred against European culture. This expansion, under Manifest Destiny, is a rejection of Whig Party suggestions that want to improve and modernize the economy and society instead of expanding the region. Slavery was abolished in all the states of the North (north of the Mason-Dixon line separating Pennsylvania and Maryland) in 1804, but remained in the southern states due to the high demand for cotton from Europe.
After 1820, a series of compromises delayed the dispute over the issue of slavery. In the mid-1850s, Republican forces seized political control over the North and promised to stop the expansion of slavery, which indicated the abolition of slavery. The presidential election in 1860 won by Republican Abraham Lincoln made eleven slave states detach and established the Confederacy in 1861. After four years of bloodshed, the Union, under President Lincoln and Ulysses S. Grant as the commander of the Commander defeated the South with Robert E. Lee as his most famous general. Eventually slavery was wiped out and the South became poor. In the era of Rekontsruksi (1863-77), the United States ended slavery and expanded its legal and voting rights to former slaves (African Americans who had been slaves). The national government became stronger, and because of the Fourteenth Amendment, the government now has a real task to protect individual rights. The reconstruction ended in 1877 and from the 1890s to the 1960s the Jim Crow system (segregation) caused blacks to be in political, social, and economic inferiority. The whole of the South suffered poverty until the second half of the 20th century, as the North and West grew and prospered rapidly.
The United States became an excellent industrial force in the early twentieth century by an explosion in the number of entrepreneurs in the North and the arrival of millions of immigrant workers and peasants from Europe. The national rail network is completed, and large-scale mines and factories are industrializing the Northeast and the Middle East. The middle-class discontent of traditional corruption, inefficiency, and politics sparked the Progressive movement from the 1890s through the 1920s, prompting reforms and allowing women's voting rights and the prohibition of alcohol (revoked in 1933). Although initially neutral in World War I, the United States declared war on Germany in 1917, and funded the Allies to victory a year later. After decades of prosperity in the 1920s, the collapse of Wall Street in 1929 marked the start of a worldwide Great Depression over a decade. Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt becomes president and implements his new program, New Deal, for aid, recovery and reform, which defines modern American liberalism. After the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, the United States entered World War II with the Allies and helped defeat Nazi Germany in Europe and defeat Japan in the Far East.

After World War II, the United States and the Soviet Union emerged as competing superpowers and started the Cold War. The two nations are fighting indirectly in arms rivalry and the space race. The foreign policy of the United States during the Cold War centered on the destruction of Communism, and the country participated in the wars in Korea and Vietnam to achieve this goal. Liberalism won many victories during the New Deal and also in the mid-1960s, especially in the success of the civil rights movement, but conservatism again developed in the 1980s under Ronald Reagan. The Cold War ended after the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991, making the United States the sole superpower. Entering the 21st century, international conflict is centered around the Middle East and rises sharply following the 9/11 attacks and the War on Terrorism declared thereafter. The United States suffered its worst economic recession since World War II in the late 2000s, followed by slowing economic growth during the 2010s.