SEC S20W3 || Morphological Anemias - Module 3

Defines Morphological Anemia
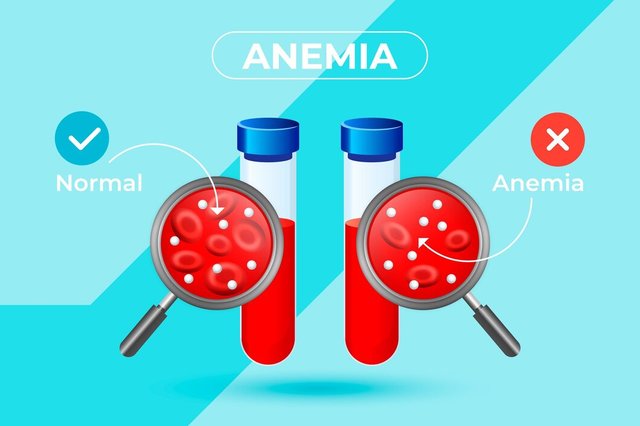
As we have studied last week, Anemia can be defined as the deficiency in the number or quality of red blood cells (RBCs) or hemoglobin due to which the ability of the blood to carry adequate oxygen to the body’s tissues reduces. The common symptoms of anemia are fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, dizziness, and pale skin.
When anemia classified on the basis of morphology by examining under the microscope, the shape ,size or morphology of Erythrocyte cells or red blood cells (RBCs) is referred as Morphological Anemia. The cause of anemia can be diagnosed by looking into the RBC size, shape, and color. Morphological anemia can then be grouped into three main categories based on size:
- Microcytic anemia
- Normocytic anemia
- Macrocytic anemia
Microcytic anemia: this type of anemia happened when RBCs are smaller, often due to iron deficiency, thalassemia, or chronic diseases.
Normocytic anemia: this type of anemia happened when RBCs are normal in size but in a reduced number are often caused by acute blood loss, diseases in general or damage to the bone marrow.
Macrocytic anemia: this type of anemia happened when RBCs are larger than normal; the most common causes include deficiencies of vitamin B12 or folate, liver disease, or alcoholism.
This tends to narrow down the differential diagnosis and might actually lead one to further diagnostic testing.
Have you ever had anemia? Attach evidence
They injected venofer drips (Fe drips) to recover the condition and after taking 3 drips in a month hemoglobin level reached to 10.3 that was near to normal.
As this happened 16 years ago so I don't have any medical evidence for it. But its quite normal situation when a woman has pregnancy.
Pathophysiologically, what happens with anemia?
- It can be caused by decreased production of RBCs or
- by an acceleration in the destruction of RBCs, or
- it may be the result of blood loss.
Its causes due to reduced production include bone marrow dysfunctions and also due to nutritional deficiencies such as iron deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency, or folate deficiency, or any other chronic disease that interferes with the production of RBCs.
The above causes increase RBC destruction, or hemolysis. Inherited conditions include sickle cell anemia, while autoimmune disorders include hemolytic anemia.
Loss of blood, whether it is acute or chronic, means depletion of RBC levels and further reduction in the delivery of oxygen to tissues.
The body compensates for this through increased heart and respiratory rates and even increases the production of erythropoietin, stimulating RBC production. The body also shunts blood flow to vital organs. Despite all these attempts, tissue hypoxia, however, brings on the most general manifestation of anemia, namely weakness, fatigue, and breathlessness.
For each type of anemia, there is another mechanism of pathophysiology; however, the common effect is to decrease oxygen transport to tissues.
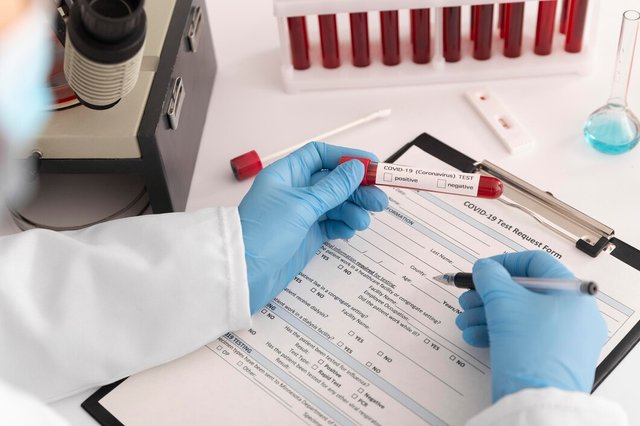
Clinical case
A woman arrives at the emergency room of the Ruiz y Páez Hospital Complex, unconscious and with signs of paleness. The doctor tells her to perform a complete hematology and an HCG. The results of the homology indicate hemoglobin 9 g/dl, MCV 71 fL, HCM 24 pg, CHCM 27 g/L and positive HCG. Classify the anemia morphologically and explain what you understood about the clinical case.
Explanation:
| SNo | Test | Result | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hemoglobin(Hb) | 9g/dl | low Hemoglobin (normal range: 12-15 g/dl) |
| 2 | MCV | 71 fL | Microcytic anemia (normal range: 80-100 fL) |
| 3 | HCM | 24pg | Hypochromic Anemia (normal range: 27-31 pg) |
| 4 | CHCM | 27 g/L | Low CHCM (normal range: 32-36 g/L) |
| 5 | HCG | positive | Pregnant |
Clinical Case Interpretation:
This woman patient, presents with:- Pregnant women as HCG test is positive.
- facing severe anemia as she is pale and (Hb 9 g/dl)
- Have Microcytic (MCV result low), hypochromic (HCM is low) anemia, possibly due to:
- Iron deficiency
- Chronic disease
- Thalassemia
In this case the doctor's request for both hematology and HCG tests suggests suspicion of pregnancy-related complications. The patient's all symptoms (unconsciousness, paleness) and then laboratory test results (severe anemia) may indicate:
- Her Pregnancy-related bleeding or hemorrhage
- May Placental abruption
- May Ectopic pregnancy
Immediate medical attention is necessary to:
- Stabilize the patient
- Determine the cause of anemia and bleeding
- Provide appropriate treatment for pregnancy-related complications
In this case further testing, would be essential to confirm the diagnosis and guide management.
This is the end from my side and I have tried to give answers of all questions. I would like to invite @sualeha, @artist1111 and @roohiasif99 for the contest .

Your professional and diligent efforts are instructive for us. This analysis of anemia will help many. Good luck for the contest.
Thanks for your valuable feedback ♥️
Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.
Upvoted. Thank You for sending some of your rewards to @null. It will make Steem stronger.
Hi friend excellent explanation cover up all the aspects.best of luck.
Hello dear... it was a pleasure to read your post in this contest... your anaemia experience was a valuable lesson and important information.
Here we learn, share and inspire.
I wish you success in this challenge.
Greetings
Thanks @aviral123 for the support