HOMEOSTASIS IN CELLULAR METABOLISM
Homeostasis refers to an organism' s tendency or drive to maintain the normalcy of its internal environment. Including maintaining the concentration of nutrients and metabolites within relatively strict limits. 
 A good example is glucose homeostasis. In the face of widely varying physiological conditions, such as fasting or exercise, both of which tends to lower the blood glucose or following the consumption of carbohydrate diet the raises the blood glucose concentration, the human body activates hormonal mechanism that operate to maintain blood glucose within narrow limits 80-100mg/dl or 4.4-5.5mmol/L. Hypoglycemia (low blood glucose) stimulates the release of gluconogemic hormones such as glucagon and the synthesis of glucose in the liver (gluconogenesis),followed by the release of glucose into the blood. On the other hand , hyperglycemia (elevated blood glucose) stimulate the release of insulin ,which promotes the uptake of glucose and it's utilization ,storage as glycogen, and conversation to fat.
A good example is glucose homeostasis. In the face of widely varying physiological conditions, such as fasting or exercise, both of which tends to lower the blood glucose or following the consumption of carbohydrate diet the raises the blood glucose concentration, the human body activates hormonal mechanism that operate to maintain blood glucose within narrow limits 80-100mg/dl or 4.4-5.5mmol/L. Hypoglycemia (low blood glucose) stimulates the release of gluconogemic hormones such as glucagon and the synthesis of glucose in the liver (gluconogenesis),followed by the release of glucose into the blood. On the other hand , hyperglycemia (elevated blood glucose) stimulate the release of insulin ,which promotes the uptake of glucose and it's utilization ,storage as glycogen, and conversation to fat. 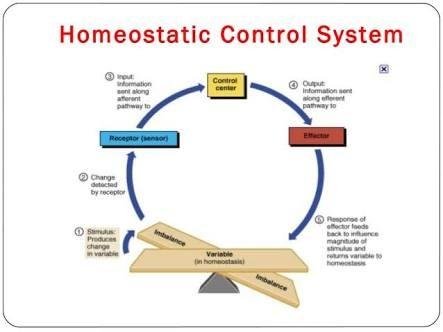
 all pix @google.MAINTAINING THE NORMALCY OF INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT.
all pix @google.MAINTAINING THE NORMALCY OF INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT.
Thanks for reading
I am @tns.....
Long live steemiteducation
Long life science
Long life steemit Nigeria
This is good and i really commend your efforts,
Looking forward to more on the details on ur further posts in terms of feedbacks ,
Mechanism of effectors and receptors.
Welldone sir
Good information here, @tns1
@originalworks
Homeostasis really have to been carried out on a daily basis in other to maintain a proper internal environment......
@originalworks