Sugars - essential knowledge and helpful tips for active people
This article is big one but you can find a lot of answers to questions about sugars (what? how? why? when? how much?) so check it out and I assure you'll find some useful knowledge that anyone can use to achieve their goals in sport or improve health. You can also look for bold headings to find what you need without reading everything. Enjoy :)

image source
CARBOHYDRATES
Carbohydrates, or sugars are compounds, that are essential for human body to produce energy needed for its functions, like muscle work or activity of brain, which controls every process. 1 gram of carbohydrates provides 4 kcal of energy. We know their basic function yet carbohydrates are not equal and we know many of sugar forms. The most common way is to distinct two forms - complex and simple sugars. Simple ones are these, that does not require energy input, which allows quick absorption, whereas complex sugars do require a bit of work from our body and thats what makes them good energy source, that is spread over time. Sources of simple sugars are for example fruits, vegetables and honey and complex ones come from pasta, bread, groats, bran, rice and legumes.
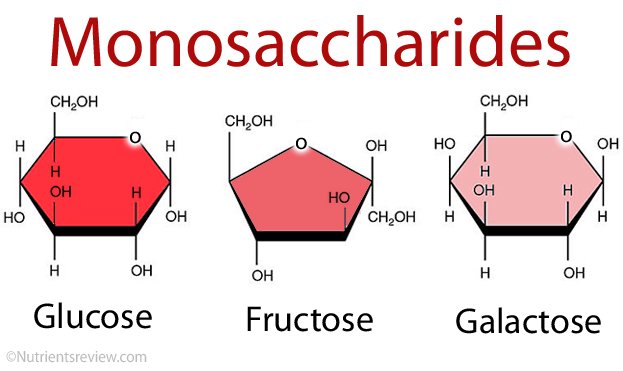
image source
glucose - common sources of glucose are vegetables, fruits and honey.
fructose - is mainly found in fruits as well as in honey.
galactose and mannose are rarely found separated from other carbs. Ribose is component of ATP (high energy molecule that stores energy our body needs to do everything), vit B12 and also rybonucleic acid (RNA).
Glucose is the only source of energy for brain cells and erythrocytes, which makes it necessary for everyone. Thanks to it our brain cells are nourished and oxygenated.
Fructose can be transformed in liver into glucose and become energy supply called glycogen. If we provide our body with too much of fructose, it may lead to increased synthesis of triglycerydes in our liver, which can cause atherosclerosis as well as other cardiovascular problems. Also consuming fructose leads to decreased sensivity of leptin - body satiety index which causes us to eat more than we should.
Simple carbs have much use in sport, because of how quickly they get into bloodstream to provide energy. Yet we should be careful, when using pure glucose supplements, because it directly increases glucose level in bloodstream. And why do we care ? Because it makes our body produce huge amounts of insulin, which can cause our liver to release too much sugar and lead to hypoglycemia, which makes it really hard for us to be physically active. As mentioned before:
- glucose is energy source for brain and that means it has to be constantly provided. Brain doesn't store it in form of glycogen. Lack of it impairs work of our central nervous system and that makes it hard for our muscles to work. To prevent hypoglycemia we should mix pure glucose with starch.

image source
saccharose - 1 particle of glucose connected to 1 particle of fructose
lactose - 1 particle of glucose connected to 1 particles of galactose
maltose - 2 particles of glucose connected to each other
Few words about saccharose: Aquired from white beet or sugarcane. Its part of honey, we sweeten coffee or tea with it and we add it to cakes and other kinds of food.
Lactose or milk sugar is found (as name points) in milk products
Maltose or malt sugar is found in beer and bakery products
Remaining disaccharides are celebiosis and trehalose. Celebiosis is aquired in microbiological process of cellulose decomposition and trehalose is found only in mushrooms.
Oligosaccharides also known as gas producing sugars and they are found in seeds of legumes.

image source
starch - is made of few particles of glucose connected in branched chains. Its source of plants energy in same way as glycogen is energy source of animals. Its mainly found in wheat seeds, potatoes and legume seeds (peas, beans, soy, lentils etc.)
glycogen - is made of many particles of glucose and is energy storage of animals. Its mainly found in liver and muscles.
Both starch and glycogen is easily absorbed by human body.cellulose - usually our body is not able to absorb it. Its also known as fiber - compotent of plants cell membrane. Its very important carbohydrate in our diet, because it helps our intestinal peristalsis function properly and by binding cholesterol and other byproducts of metabolism, such as heavy metals. In other words it acts, like vacuum cleaner for our body. It has detoxifying properties and prevents atherosclerosis as well as helps us to maintain body weight. Its very important in sport when your goal is to reduce weight before competintion or just to get more ripped. Recommended daily dosage ranges from 25 to 40g. Rich sources of fiber are: wheat bran, fruits and vegetables.
resistant starch - is not found in natural food but is made in technological food processing. When starch is exposed to high temperature in dry environment it causes damage to its structure. Its mainly found in grain from full milling. Fact that its not digested by our body doesnt mean it has no use for us. It acts, like prebiotic (being used as food for good bacteria in our intestine). Another interesting fact is that unripe, green bananas work in similar way to resistant starch, because they contain fructans, which are also found in garlic, leek, onion and chives.
inulin - is polysaccharyde that is not digested by human enzymes. Its found in rhizomes, chicory tubers, tuberous sunflower and dandelion.It also has prebiotic properties. Why I keep writing about these ? Because its properties help our bacteria to multiply, so they can help and do good job in our intestine. Their job is to regulate level of cholesterol in blood and help us absorb minerals, that are important for everyone to function properly. Inulin prevents constipation, atherosclerosis as well as helps us in weight reduction and prevents cardio vascular disease.
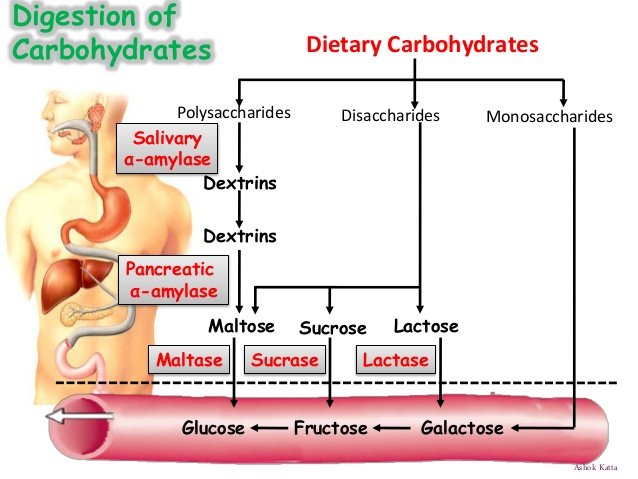
image source
All of complex carbohydrates have to be dissolved into glucose, to make it possible for our body to absorb them from digestive tract into bloodstream, from where they can be distributed, to where they are needed.
After eating meal that contains carbs, our level of glucose increases and when unused its being stored as glycogen. When glucose level drops our body uses stored glycogen thanks to release of adrenaline and and glucagon. Glycogen supplies are limited to 300g for people, who don't work out and 600g for those who do. In body of sportsman this kind of phenomenon is called supercompensation. Because of limited storage space for glycogen in our body, extra carbohydrates are transformed into fat and thats how we gain weight. Our liver can store glycogen that equals to 2% of its mass and after approximately 24 hours its reserve is completely empty. Muscles have greater mass than liver and thats why sportsmen, who have well built muscles can store even more glycogen (600 - 1000g).
Carbohydrates are cheapest, easily digestible, well absorbed and most economical source of energy, because our body uses small amounts of oxygen to consume them. They can also be metabolised and provide energy in anaerobic conditions, while working out in anaerobic way as well as in aerobic conditions.

image source
They can ofcourse easily become an enemy, when we consume more than we need. We can easily overdose them by eating products, like white sugar, cakes, candies, bars and milk chocolate.
According to World Health Organisation (WHO) - our daily diet should contain 50 - 65% of carbs. People who are physically active should aim to consume 4 or 5 times more carbs, than proteins and fats. In speed and strength training we run low on oxygen, so we should try to lower our dosage of fats and proteins and keep ratio of proteins to fat and carbs at 1 : 0,9 : 4. In endurance training we should make that ratio 1 : 0,8 : 5. In each discipline carbs condition our so called special endurance. How long we can keep physical activity depends on numbers of stored glycogen in our muscles, and it depends on how much carbs we have eaten. 5 days before sport competition we should increase our physical activity in way that allows us to deplate our glycogen supplies and then resupply them by proper diet. 2 days before competing we should aim to decrease numbers of consumed fiber and drink a lot of salted drinks.

image source
Grain products such as flour, pasta, groats, potatoes, pods and fruits. These products may cause us to feel heavy, so we should avoid them 1 hour before and during training.
Still starch should be 64% of all carbs that we consume in daily diet and simple sugars should be 10% of our daily calories.
Final stage of transformation of basic nutrients which are: proteins, fats and carbs is common for them. Everything starts with acetylcoenzyme A, which is being fueled by carbs. If we do not have enough of glucose, process of transformation is slowed and causes part of acetylcoenzyme A to be transformed into ketone compounds that provide energy. If there is too much of these compounds, our body acidity level increases and that makes it hard for our body to get enough of oxygen into its tissues. We should be also aware that deficit of B1 vitamin (tiamine) makes process of creating acetylecoenzyme slower.
Answer is simple. Simple carbs as they provide energy faster and easier, without using greater amounts of oxygen. Good pre workout products are fruits, juices and vegetables. They are easily absorbed and don't overload your digestive system with work. That makes it easier for our body to focus on muscle work and pumping blood so our effectiveness increases. Definitevely bad products to eat before workout are dark bread, beans, peas, cabbage, which are hard to digest and bloating.
Its important to rebuild supplies of glycogen by consuming products rich in starch: grits, rice, bread, legumes, fresh vegetable salad. With these you can easily provide your body with nutrients lost during workout and repair damaged muscle tissue. For physically active people best fruits to eat are: strawberries, blueberries, gooseberries, raspberries and currants. When you cant find them in raw form you could eat them in jam and frozen form or get some easily obtainable citrus fruits.
During workout you can drink fruit juice, vegetable juice or tea with sugar or honey.
If you work out few times a day, your meals shoud be prepared by boiling, stewing or steaming, because it makes them easily digestible. Raw, fried and bloating meals are best consumed after workout. Best way to fry is to use teflon frying pan, because you don't need to add oil and extra fat into your meal.
Contestants can feel jitters, which can cause constipation. In situation like that, you should aim to consume more fluids, drinks and raw fruits as well as groats. Other contestants can get diarrhea, because their nervous system is very active. If you happen to be in that group, you should try eating rice, warm boiled milk, baked apples, blueberries juice, old white bread, puree and dried plums compote.
To build muscles you need excess calories. Here is an example:
Male, age 19-30, 85kg weight, who works out with medium intensity 4 times a week should consume 3450 kcal. If he wants to increase muscle mass he should raise his caloric surplus by at least 500 kcal, which summed up gives us 3950 kcal. If he uses 1 : 0,9 : 4 nutrient ratio he should consume about 153g of proteins, 137,7g of fats and about 612g od carbs; from which 64% should be starch.
IF you want to reduce your weight and get ripped your goal should be to reduce calorie intake. Good amount is -500 calories, but if you want to see results faster and don't care too much about loosing some muscles in process you can reduce calorie intake further.
Feel free to ask any questions that you may have after reading :)