ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION – IT’S NOT A SHAME TO TALK ABOUT IT (SFW - NO GRAPHIC IMAGES)


INTRODUCTION


Erectile dysfunction (ED) is one of the most common diseases affecting men yet it is also sometimes a very taboo subject to talk about. It is defined as the inability to achieve or maintain an erection which is sufficient enough for penetrative sexual intercourse or in general a satisfying sexual performance. A few incidences of ‘failure to perform’ are actually pretty common in a man’s life and usually nothing to worry about. But a persistent incapability of a man to have an erection is something that can cause a substantial effect on his quality of life. The incidence and impact of ED are usually underestimated. Whether we like it or not, the biology and hardwiring of human males makes them extremely sensitive and conscious when it comes to matters of an adequate sexual performance. The inability of men to perform sexually is believed to cause a huge psychological impact on them but it also affects their partners and their relationships. The most shocking thing about ED is its prevalence. It is believed that about 50% of men over the age of 40 are affected by it in various degrees. ED has a very strong association with age. It may begin in some cases from even the age of 20 and its incidence rate increases proportionally to the increasing age of a man. It is believed that today up t 30 million men in the USA are affected by ED.

HOW DOES AN ERECTION HAPPEN?

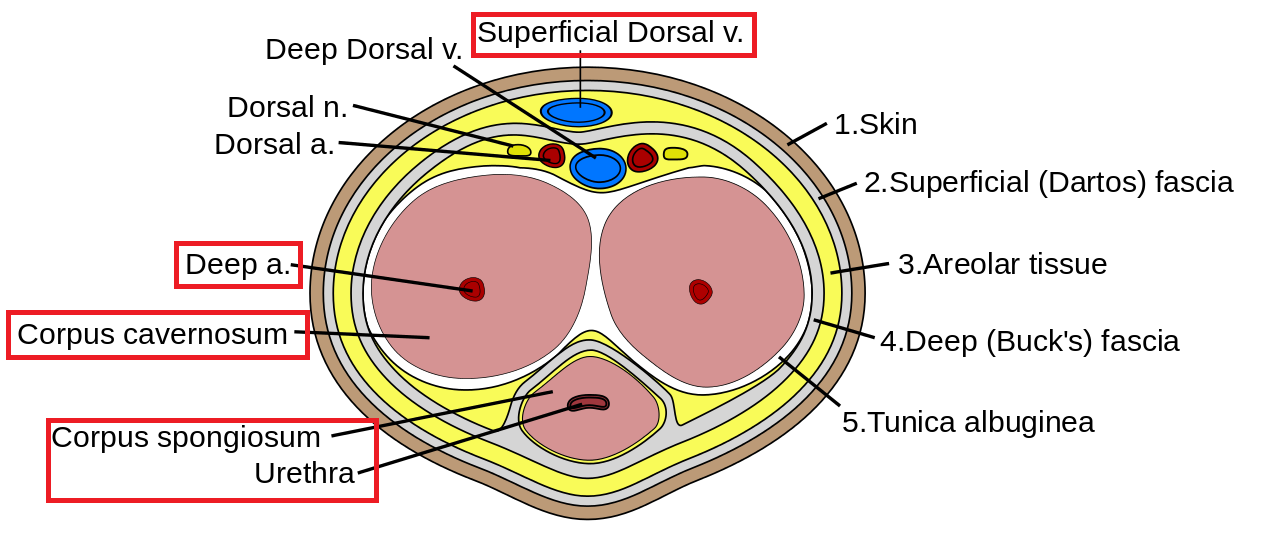
I know that the answer might seem quite obvious, but let’s try and get a bit deeper. To understand the mechanisms of an erection we must first know a few basic details about the anatomy of the penis. The above picture is a cross section of the human penis. As you can see, it is made up of three main parts. Two identical structures called corpora cavernosa which are found next to each other approximately in the centre of the penis and a third structure lying under them called the corpus spongiosum. The latter, is not particularly involved in erections but the male urethra runs through it and therefore it is involved in urination and ejaculation. Other important structures of the penis are the Superficial Dorsal vein, the big vessel that we all have on the superficial part of our penis and the Deep arteries which run through the corpora cavernosa and fill their spongy tissue with blood during erections.
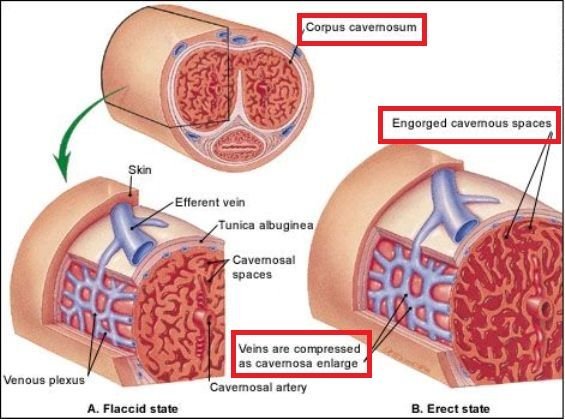
An erection is a process which involves the Central and Autonomic nervous systems and of course, the vascular system. Upon sexual stimulation (from tactile, olfactory and visual stimuli) the Parasympathetic Nervous system (part of the Autonomic) is activated. Sacral branches of the Parasympathetic Nervous system release a neurotransmitter called Acetylcholine which in turn causes the release of a substance called Nitric Oxide (NO) in the vessels of the corpora cavernosa. NO acts as a vasodilating substance, in other words it makes the vessels inside the corpora cavernosa to relax, enlarge and fill with blood and therefore causing an erection. When these vascular spaces fill with blood they also compress some of the veins of the penis, preventing blood from draining out and therefore ‘trapping’ it inside the erect penis. During the male orgasm, the Sympathetic Nervous system takes over leading to ejaculation and the subsequent loss of the erection.

WHEN THINGS GO WRONG

Many pathophysiological mechanisms have been suggested to be hiding behind ED but we are not yet able to point at exactly what goes wrong. Most commonly there is a dysfunction in the release of the vasodilating substance NO. As a result the vascular spaces inside the corpora cavernosa cannot properly relax and not enough blood flows into them resulting in an inadequate or completely absent erection. This is why most drugs against ED such as Sildenafil (Viagra) target the NO mediated pathway of erection. The decreasing levels of testosterone with age are also thought to play a role, even though the exact mechanism is not completely understood.

Source
Even though the pathophysiology of ED is still not very clear, the etiology is actually quite well known. Causing factors are usually divided into two large categories: organic and psychogenic. Organic causes are by far the most common and include factors such as smoking, alcohol, diabetes, hypertension and atherosclerosis. ED is also associated with endocrinologic abnormalities, prostatic hyperplasia, respiratory diseases, obesity and neurological diseases. Psychological factors (depression, performance anxiety etc) can play a role, especially in younger patients, but the medical community agrees that ED is usually a combination of many factors together rather than the result of a single etiology. Diagnosis is made through a detailed history taking from the patient and various laboratory tests.

HOW IS ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION TREATED

The key in treating ED is to identify the possible causing factors and treat them separately. In some occasions the sexual partner may also be involved and the couple may go into sexual counselling if they desire. A large percentage of men restore an acceptable erectile function through lifestyle modifications and oral medication. The most important factor is to improve the overall vascular health of the body. Weight loss and frequent moderate exercise have been proven to help patients substantially, sometimes even when used as the only treatments for ED. A pharmaceutical control of hypertension and diabetes are also important to improve the patient’s general health but also decrease the incidence of ischemic events during sexual intercourse. Lastly, the most frequently used medications targeting ED directly are the so called Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors such as Viagra and Cialis. These are usually taken before sexual intercourse and they still require sexual stimulation to give the man an erection.
Other methods are also available, even though most men will not need them. Vacuum pumps, constriction devices, intracavernosal injections of medication and inflatable penis prosthesis can be used when other methods fail. Surgical procedures are only done in younger patients who suffer from ED because of trauma and neurological damages. At the moment new medical approaches are being considered and developed such as a tissue engineering technique that aims in rebuilding the corpora cavernosa. No matter what the future holds for this disease, it is important for men not be embarrassed to talk about it with their doctors. Erectile Dysfunction is an extremely common condition with very efficient treatment options which can help people maintain healthy sexual relationships.
==============================================================================
Sources:
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/444220-overview#a2
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022534705679001
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0090429597002380
==============================================================================

For many more articles like this, follow me @nulliusinverba
nice post!
Thank you @francis228
You are absolutely right that many men are needlessly ashamed to talk about ED, which is really just a medical condition. A survey in 2018 found that over 40% of men are embarrassed to talk about erectile dysfunction, even with their doctor. This can prevent them from getting necessary help.
SOURCE:
https://edtreatment.info/ed-impact-study/