Understanding Hyperthyroidism: A Comprehensive Overview
Hyperthyroidism is a condition characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, which produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. This can lead to a variety of health issues, and understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing the condition effectively.
Causes
Hyperthyroidism can be triggered by several factors, including:
Graves' Disease: The most common cause, an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland.
Thyroid Nodules: Overactive lumps on the thyroid can produce excess hormones.
Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid can lead to a temporary increase in hormone production.
Excessive Iodine: High iodine intake from diet or medications can stimulate hormone production.
Symptoms
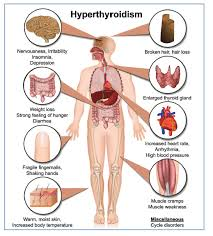
The symptoms of hyperthyroidism can vary widely but often include:
Unexplained weight loss
Rapid heartbeat (palpitations)
Increased appetite
Anxiety or irritability
Sweating and heat intolerance
Tremors in the hands or fingers
Menstrual changes in women
Fatigue or muscle weakness
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of:
Physical Examination: Checking for symptoms such as rapid heartbeat or tremors.
Blood Tests: Measuring levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
Imaging Tests: Ultrasound or radioactive iodine uptake tests can help assess thyroid function.
Treatment Options
Managing hyperthyroidism often involves one or more of the following approaches:
Medications: Antithyroid drugs, like methimazole, can reduce hormone production.
Radioactive Iodine: This treatment destroys overactive thyroid cells, reducing hormone levels.
Surgery: In some cases, removing part or all of the thyroid gland may be necessary, particularly if there are large goiters or cancer concerns.
Living with Hyperthyroidism
Managing hyperthyroidism requires regular monitoring and adjustments to treatment. It's essential to work closely with healthcare providers to find the best management strategy. Lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques, can also help in managing symptoms.
Conclusion
Hyperthyroidism can significantly impact daily life, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals can lead healthy, active lives. If you suspect you have symptoms of hyperthyroidism, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate testing and management.
Stay informed, and prioritize your health!