The Importance of Geometric Properties in Beam Design
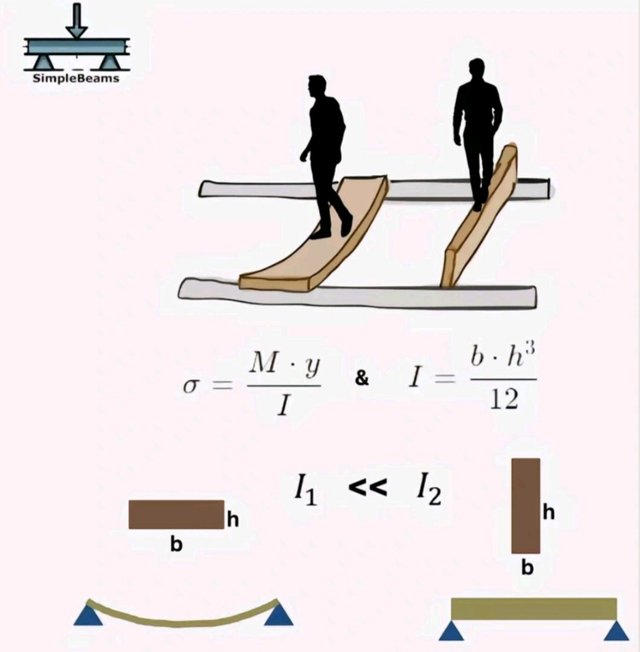
Figure : Comparison of beam stiffness based on orientation and moment of inertia. Vertical orientation provides higher stiffness due to the larger moment of inertia.
In structural design, understanding how geometric properties influence beam behavior is essential for ensuring efficiency and safety. This fundamental concept has critical applications in civil and mechanical engineering.
Moment of Inertia: A Key to Beam Stiffness
The illustration demonstrates how the moment of inertia (I) directly affects a beam's stiffness under load.
where:
b: base of the cross-section,
h: height of the cross-section,
The equation shows that the moment of inertia increases exponentially with the height . This means that increasing the height of the cross-section results in a much stiffer beam.
Why Does It Matter?
When comparing beams oriented horizontally and vertically, a beam with its larger dimension in the vertical direction (height ) can carry more load with less deflection. This is because:
This translates into more efficient designs, where materials are used optimally, reducing both cost and structural weight.
Practical Applications
This principle is applied in:
- Bridges: Designed with "I-beams" to maximize stiffness.
- Buildings: Using columns and beams that resist loads with minimal deformation.
- Railways and Transport: Where strong yet lightweight structures are required.
Conclusion
This analysis highlights how geometric properties and their correct application can make a significant difference in structural efficiency. Optimizing these variables not only reduces costs but also contributes to safe and sustainable design.