Voltage Sources: Energy Conversion and Examples
We use them every day, but no one really gives them much thought. What are we talking about? Why, voltage sources, of course! Batteries and generators are two of the most common sources of voltage that power our daily lives. We'll look at them in detail to see how they work.
Voltage And Voltage Sources
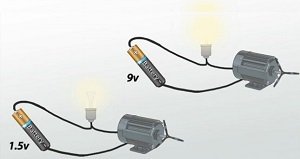
The higher the voltage in a power source, the stronger the energy current.
Voltage sources are the unsung heroes of our electronic lives. Without them, electrons would never be motivated to power the circuits in our cell phones, laptops, TVs or any other electronic gadget. You may have already guessed that batteries are one type of voltage source. Another type is the generator at the power plant that delivers electricity to your home. We're going to look at these two types of voltage sources in detail to better understand how they work, but first we need to talk about voltage.
Voltage is the potential of a group of charged particles to do work in an electric circuit. In practical terms, electrons at a higher voltage will light a light bulb more brightly or spin a motor faster than will electrons at a lower voltage. To compare this behavior to something a bit more tangible, we can say that voltage acts a lot like water pressure. A high-pressure fire hose will spin a bicycle wheel a lot faster than will a low-pressure garden hose. Just like pressure pushes water through a pipe, voltage pushes electrons through a circuit.
