What is Blockchain Architecture?
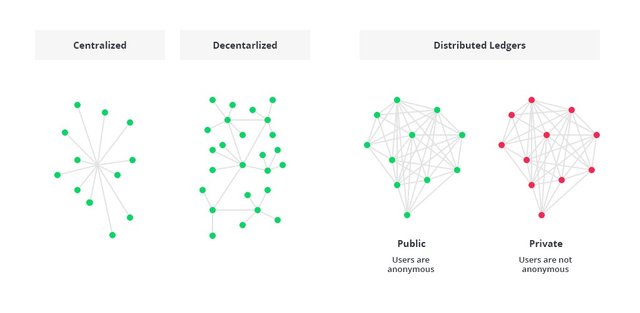
A blockchain is a chain of blocks which contain specific information (database), but in a secure and genuine way that is grouped together in a network (peer-to-peer). In other words, blockchain is a combination of computers linked to each other instead of a central server, meaning that the whole network is decentralised
.
To make it even simpler, the blockchain concept can be compared to work done with Google Docs. You may recall the days of tossing over doc. documents and waiting for other participants to make necessary edits. These days, with the help of Google Docs, it is possible to work on the same document simultaneously.
The blockchain technique allows digital information to be distributed, rather than copied. This distributed ledger provides transparency, trust, and data security.
Blockchain architecture is being used very broadly in the financial industry. However, these days, this technology is employed not only for cryptocurrencies, but also for record keeping, digital notary, and smart contracts.
Types of Blockchain Architecture
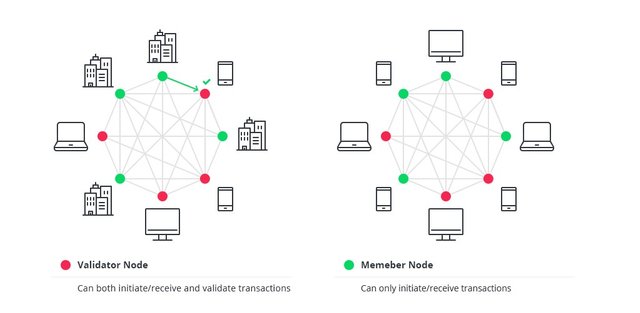
All blockchain structures fall into three categories:
Public blockchain architecture:
A public blockchain architecture means that the data and access to the system is available to anyone who is willing to participate (e.g. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin blockchain systems are public).
Private blockchain architecture:
As opposed to public blockchain architecture, the private system is controlled only by users from a specific organization or authorized users who have an invitation for participation.
Consortium blockchain architecture:
This blockchain structure can consist of a few organizations. In a consortium, procedures are set up and controlled by the preliminary assigned users.