Multi-Layered Security Approach for DNA Metaverse
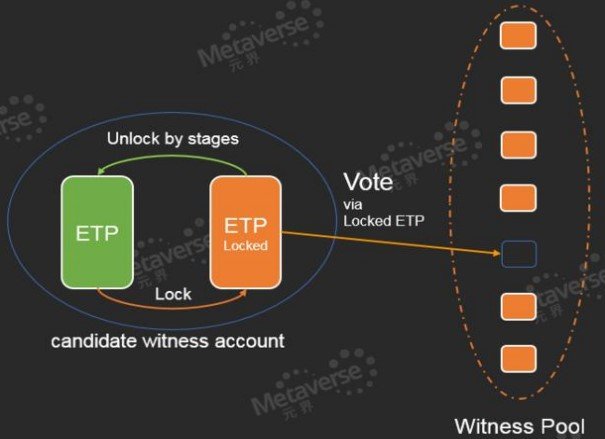
The number of DNA tokens determines the proceeds accrued from staking. It is the duration of staking. The fees of sending data feed, smart contracts cross-chain, and tokens are paid in DNA tokens. It is more difficult for the spammers to attack the system because all transactions require DNA tokens for execution. It acts as a media of exchange for the other assets and cross-chain. For smart contracts, DNA can serve as the asset collateral. The number of DNA tokens dictates the voting power in the elections of the nodes. It is weighted by the duration of staking.
Security Parameters
Security is the essential side of any blockchain project. It is a multilayered approach to security. Hardened OS setting to child, Regular, and Super nodes are provided by node security. It disables unused OS accounts, closing unused IP ports. It applies to the latest security patches.
Consensus algorithm security has shown impressive security to date. Varying degree of security have seen by POS-based algorithms. DNA's BaseChain is the Metaverse main net. It uses POW/POS hybrid consensus to maximize security. Additional consensus algorithms can be employed to increase security, such as DPOS. Permission nodes can also be employed if necessary. As similar to EOS, the DNA plan is used as a wallet/account security approach. For signing a transaction by multiple parties, multigenitures are a proven method in the blockchain world. It is often required with certain wallets, accounts, and particularly smart contracts. DNA provides a public and private key pair that sign permission to accounts. It is particularly used for a smart contract. The user's account name consists of 12 characters.

Each DNA account has two authorities, such as the owner and active. The owner has the authority to add or remove permissions to other authorities as a type of parent-child relationship. By using different permission levels, an account name can be managed in DNA. These decisions are not managed by only one person, but it is approved by several other authorities to the same account. Sender and receipt have one of the public keys. A third party also has access to the account. In disputes or commercial contracts, this setting shows real-world utility. A secured Built-in Smart Contract (BISC) is used by the base chain. It is a built-in hardened template. It is used without security breaches. DNA chain allows both BASIC and flexibility for a general-purpose smart contract. It supports greater utility and features. It also causes security issues. These additional risks are countered on the DNA metaverse platform.

For the execution of general purposes, smart contracts are recorded on the base chain. For protecting Regular and Super Nodes, Distributed Denial of Service attack (DDOS) protection is needed. It recommends relevant DDOS vendors when DNA goes live. To validate our security approach, audit the codebase, and perform penetration testing, the DNA team will seek third-party auditors. We indulge in discussions with a number of blockchain security companies. It will publish updates when it is a formal agreement. We rebuilt lightning channels between 23 Super Nodes and 529 Regular Nodes.
Author Details
Bitcointalk User: FortuneTreats741
Bitcointalk user Profile: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=2287912
Ethereum wallet: 0x94b5829A519173cCf59007C2Bd3016BBa83a4565
TG: @SAPLAKHATUN
Company Details
Website URL : https://mvsdna.com/
Twitter URL : https://twitter.com/mvsdna
Whitepaper:https://mvsdna.com/MVS%20Dualchain%20White%20Paper.pdf
Facebook URL : https://www.facebook.com/MVSDNA
Telegram URL : https://t.me/mvsdna