What is Diabetes Mellitus? What are the types & Causes of DM? What is Gestational Diabetes? Diagnostic criteria of DM with complications & treatment.
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a common endocrine disorder in Bangladesh. In 2015 one in 11 adults has diabetes. Diabetes is the fastest growing endocrine disease in our country.
Defination :
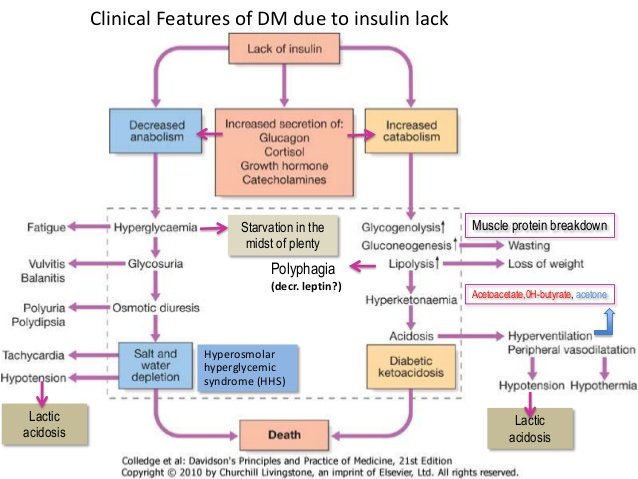
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycaemia with or without glycosuria due to absolute or relative deficiency of insulin.
Classifications of DM :
- Type-I or Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM).
- Type-II or non insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM).
- Gestational diabetes mellitus : Diabetes during pregnancy.
Causes of DM :
- Genetic defect of beta cell of pancreas because insulin is secreted from beta cell of pancreas & alpha cell secret glucagon.
- Genetic defect of insulin action.
- Infection of pancreas is called pancreatitis.
- Any neoplastic disease in pancreas.
- Acromegaly.
- Cushing's syndrome.
- Thyrotoxicosis.
Type-I DM :
- Age of onset - Usually less than 40 years.
- Duration of symptoms - Weeks.
- Body weight - Normal or low.
- Rapid death without treatment with insulin.
- Auto antibodies - Present.
- Family history of DM - Uncommon.
- Acute complications - Diabetic ketoacidosis.
Type-II DM :
- Age of onset - Usually more than 50 years.
- Duration of symptoms - Months to year.
- Body weight - Obese.
- No Rapid death without treatment with insulin.
- Auto antibodies - Absent.
- Family history of DM - Common.
- Acute complications - Hyperosmolar non-ketotic coma.
Symptoms of DM :
- Polyuria.
- Polydipsia.
- Polyphagia.
- Weight loss.
- Fatigue.
Diagnostic criteria of DM (The American Association criteria) :
HbA1c ≥ 6.5% in DCCT standard. Or
Fasting plasma glucose ≥ 7.0 mmol/L (126 mg/dl) or
2hrs after 75 gm glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dl) or
Classical symptoms with Random plasma glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dl).
Investigations :
A. In Blood -
1. HbA1c.
2. FBS, RBS or 2 hrs after breakfast or 2 hrs after 75 gm glucose.
B. In Urine -
1. Ketonuria (Rotharas test).
2. Glycosuria (Benedict's test)
C. Others -
1. CBC.
2. CXR.
3. ECG.
Complications :
A. Acute complications :
1. Hypoglycaemia coma.
2. Diabetic ketoacidosis.
3. Non ketotic hyperosmolar diabetic coma.
4. Lactic acidosis.
5. Acute circulatory failure.
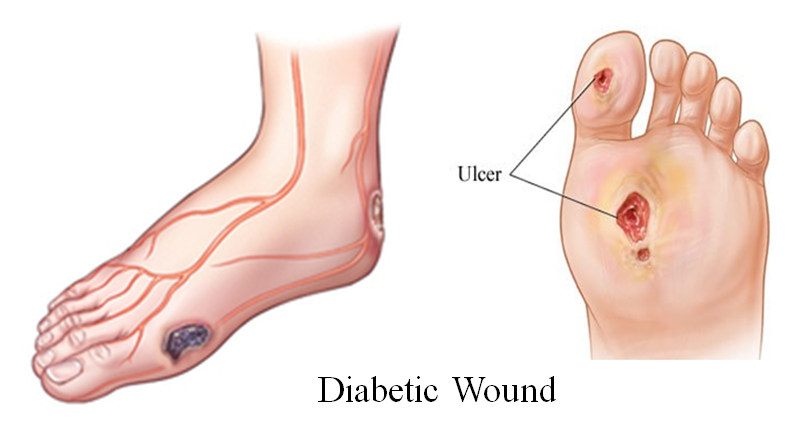
B. Chronic complications :
(a). Microvascular-
1. Retinopathy.
2. Neuropathy.
3. Nephropathy.
(b). Macrovascular-
1. MI.
2. Stroke.
3. TIA.
4. Ischemia.
@badhon8030, welcome and congratulations on making your first post! I gave you a $.05 vote! If you would be so kind to give me a follow in return, that would be most kind of you!!
Congratulations @badhon8030! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!