Marine robot: surface system
The autonomous, semi-autonomous, and remote control systems of the sea are most easily considered by groups, each of which we will create a separate publication. It is possible to distinguish between surface and subsea vehicles, a separate industry is a consumer model.
The latter does not have a high quality ballast system and is often maneuvered exclusively by machines. However, it is worth noting, in the coming years the underwater drone market will unite with VR technology: the device will help people to master one more element.
** Today we will pay attention to existing commercial and research surface systems. **
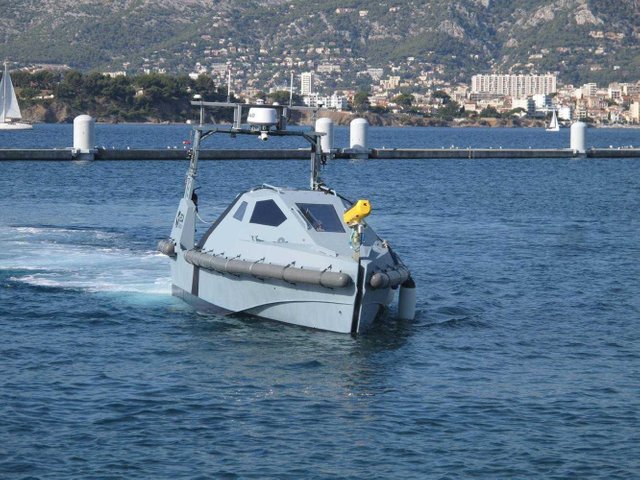
Boat-free boat
To date, there have been many developments designed for research, mine action, search and rescue operations and coastal and coastal infrastructure patrols.
For example, you can specify, for example, French MK2 Inspector: this device is able to form 2D and 3D images from the seabed at a speed of about 10 knots. Similar devices are used, for example, to search for debris during search and rescue operations.
A similar system is also available, for example, in a fire configuration. Most of these boats can function in a "habitable" mode, tele-managed and autonomous.
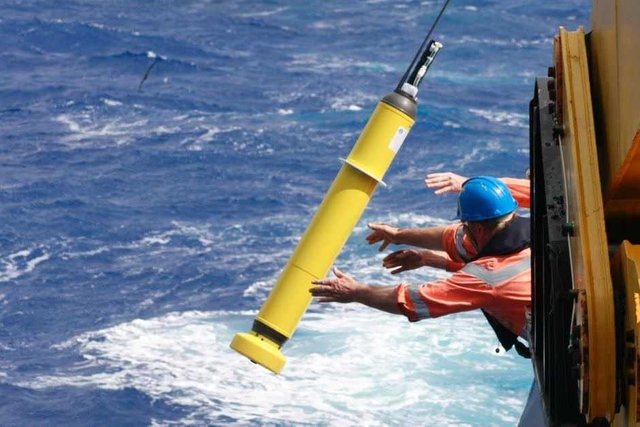
Robotic buoy
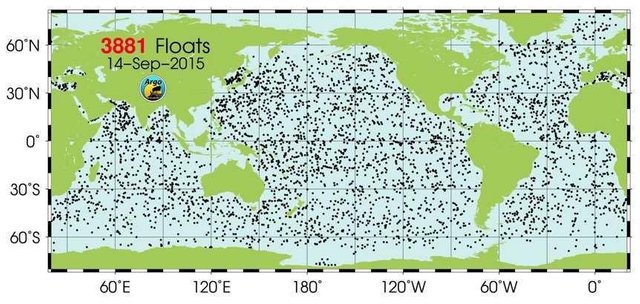
Robot buoys are used to assess environmental conditions and oceanographic research. The most remarkable development from a scale point of view is the ARGO complex, which includes more than 3.8 thousand research buoys, the distribution geography shown in the figure above.
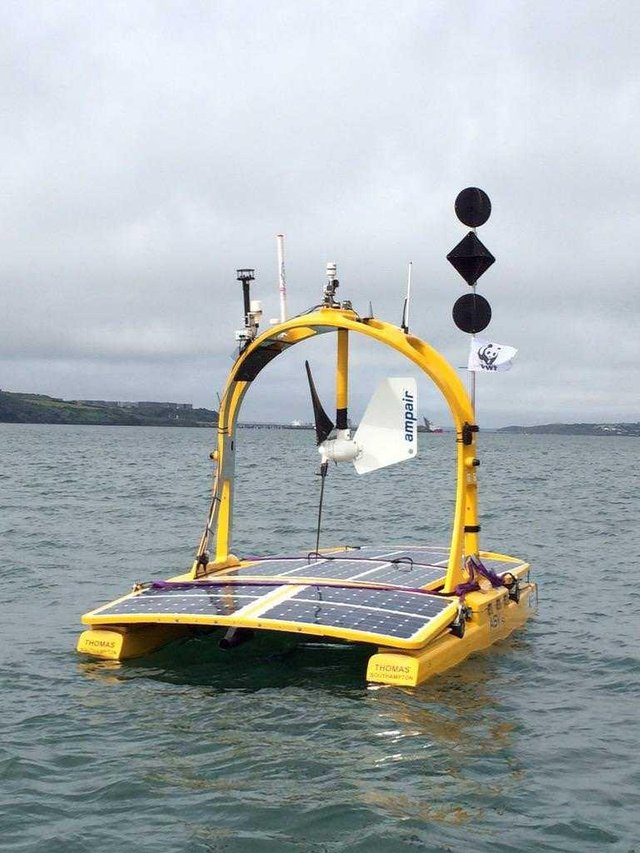
Measurement and mobile communications platform
This robot device serves to measure the state of the environment, as well as a mobile communications platform that provides undersea robotic connections by research vessel or ground control center.
As an example of such a system, we can recall C-Enduro Thomas, the development of the ASV Unmanned Marine System. The system weighs around 350 kg develops speeds up to 13 km / h, is powered by solar batteries and wind generators and provides complex ground communications with underwater robots.
Remotely controlled robots for water saving
In recent years, such systems have become popular. An example is Emily, the development of A & M University of Texas. This device can accelerate up to 32 km / h and continue to float up to 5 people. One device time "swim" - about 20 minutes.A similar system, or rather, U-Safe remote control rescue ring was developed by the Portuguese company Noras Performance.
Autonomous Cargo Ship
Most of the robots in this category are still under development.
In 2017, Norway began the construction of an autonomous ship Yara Birkeland by Kongsberg, and in 2018 Massterly and Wilhelmsen merged to form a transport company with an autonomous cargo fleet. As expected, the first robot vessels will carry cargo along the Norwegian coast by 2020.
In addition to the main project, Norwegian Kongsberg Maritime and British Automated Ships Ltd. jointly developed the Hrnnn unmanned vessel, designed for offshore service operations. Most likely, this robot system will handle offshore wind farm services and cargo shipments to oil and gas platforms.
The unmanned ship project is also in Rolls-Royce: it is expected that the company's robot system will go to sea by 2020. By 2017, the company will join Google. As expected, the system will provide significant savings if there is no seafarers or infrastructure for people: toilets, heating systems, cabins, kitchens, ventilation, etc. On the ship.
His own experience in the field of unmanned shipbuilding is also in Japan: manned by Japanese vessels going to sea around 2025. Among other things, Nippon Yusen also deals with the development of the system, which previously presented an algorithm to predict possible collisions at sea.
China will not be left behind, the country is also actively preparing for the era of robotic navigation.
Marine vans are optional-habitable
The Hyper-Sub Modular Platform combines an optional inhabited boat and submarine. On the surface, the system accelerates up to 61 km / h. The US military has seen the device.
Autonomous boats to assess the world's ocean acidification rates
Autonomous robots, powered by integrated photovoltaic batteries, can monitor the rate of ocean acidification, monitor marine animals and detect oil spills. Analogue from the mass of the project, more interest may be how to move the drone - Saildrone system sailing.
A floating wind farm
The floating wind farm, of course, is not a robot. However, automation and remote control systems allow you to adjust wind turbine blades suddenly, shut down the system during a storm, and to enter them at the same time as the danger has passed.
Specifically, the offshore wind farm Hywind Scotland, located 25 km from the coast of Scotland, provides energy for about 20,000 households: an efficiency of about 65% in November, December and January 2017.
According to an estimate of experts from Stanford University, in the next 10-15 years the development of offshore wind farms will become an important new trend: the system is placed on an area of approximately 3 million square kilometers (less than the percentage of Ocean World area) to provide people with 18 clean energy terawatts.
The height of the individual wind power system reaches 253 meters, the windmill is attached to the seabed by three chains of 400 tons. To put such a system possible in areas, whose depth reaches 800 meters.
This is our story of autonomous and robotic surface systems that come to a logical conclusion - next time we will talk about underwater robots and remote controlled systems.