Organisation Structure.
Span of Control :-
The number of subordinates a supervisor has reporting to him/her.
It is recommended that a supervisor has about 5/6 subordinates for effective management.
2 types of span of Control;
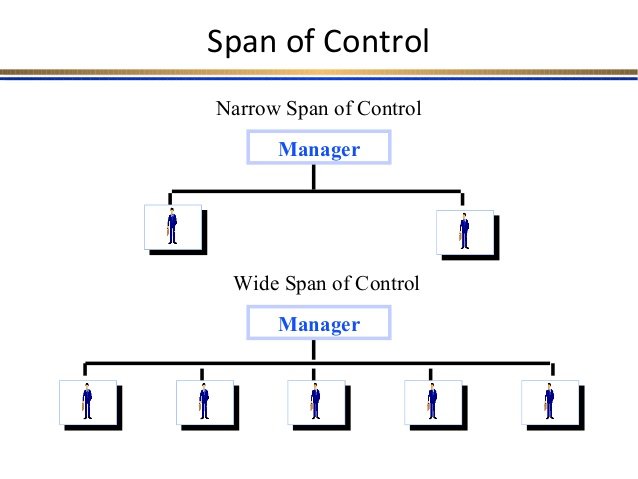
Narrow
WideNarrow
Closer and more contact with subordinate
Tight control and tight supervision
More time for other duties – planning, decision making
A lot of layers, more positionsWide
Reduced operation and administrative costs
Easier communication
Coordination problems reduced
Quicker decision making
Can cultivate higher motivation level in subordinates
Factors affecting Span Of Control:
- Competence of a manager
- Complexity of functions
- Similarity of function
- Non supervisory duties of manager
- Direction and control needed by subordinates
- Physical proximity / Geographic location
Work Specialisation:-
The degree to which the work necessary to achieve organisational goals is broken down into various jobs.
Without some specialisation, it would be difficult for the organisation to function.
People have different skills and abilities, they are usually able to carry out work effectively and efficiently if the job required a particular skill or ability they possess.

Departmentalisation:-
How jobs/ tasks are divided, grouped and coordinated.
All departments must understand and ‘pull’ together toward achieving the organisational goals.
Activities are grouped by functions e.g. Human Resources, Finance, Marketing.
Names of the departments depend on the type of business the organisation is in.
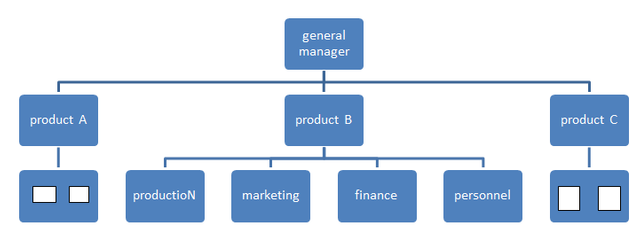
The main department designs are by;
Function.
Product.
Geography.
Matrix-customer&process.
Chain of Command (COC):-
- Unbroken line of authority form the top to the bottom of the organisation.
- Everyone is accountable to someone.
- When the COC is too long;
Complexity in communication
Message gets distorted
Depersonalized employee relations - Borderless organisation
- Team work

Centralisation:-
- Amount of authority delegated to different positions in the organisation structure.
- Decision making is focused at the top of the organisation hierarchy and lower level just carry out decisions made.
- Authority and work is little delegated.
- Advantages
Top management is aware of the happenings and overall needs, better control over activities.
Better standardised procedures and policy.
Easier to maintain secrecy.

Decentralisation:-
- Decision are made at all management levels.
- Lower level management provide input in decision making.
- Authority and work is delegated.
- Advantages
Reduces work load for Top management
Faster decisions
Better decisions
Employees learn to make decisions
Improves staff morale
Organisation becomes flexible

Formalisation:-
- Formalization refers to how standardized an organization’s jobs are and the extent to which employee behavior is guided by rules and procedures. In highly formalized organizations, there are explicit job descriptions, numerous organizational rules, and clearly defined procedures covering work processes
- Actions which are and not to be done, stated in written policies, rules, procedures
- Helps with vertical coordination
BOING! You got a 22.65% upvote from @boinger courtesy of @mamunjm!
In the fight of Humans vs Bots, @megabot defended you with 33.33% upvote courtesy of @mamunjm!
Support @Megabot by delegating SP to the bot and get a part of 98% of @Megabot's profit.
Direct delegation links : 10 SP || 50 SP || 100 SP || 500 SP || 1000 SP || Any other amount of SP
Join our discord group here.
Thank You !
This post has received a 13.53% upvote from @lovejuice thanks to @mamunjm. They love you, so does Aggroed. Please be sure to vote for Witnesses at https://steemit.com/~witnesses.