Unsupervised deep learning models used in computer vision
Introduction
After a break, I wanted to post about this emerging field of unsupervised deep learning, since it is gaining momentum and achieving good results.
The idea of this post is to give introduction and overview of the most used models, tools and useful links to kickstart your dive into an interesting part of computer vision. Unsupervised models are still being heavily researched unlike supervised model such as convolutional neural networks. In the computer vision, there are 3 main applications of these models: dimensionality reduction, clustering similar images[+image retrieval/search] and generating images.
Dimensionality reduction is used to plot high dimensional data and find some insights into data. Images can be visualized in 3D space using t-sne dimensionality reduction method and tensboard projector from tensorflow.
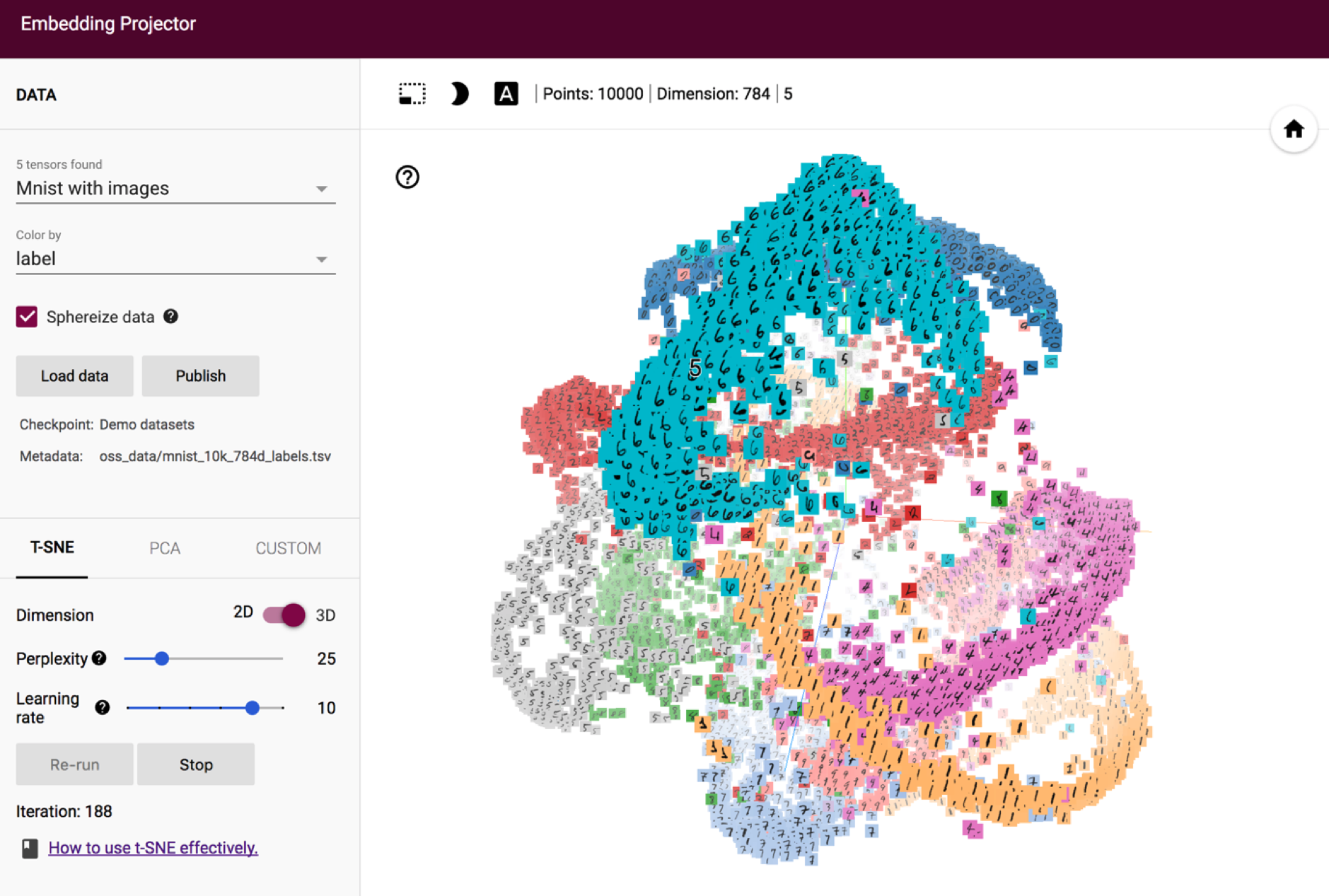
image taken from link http://projector.tensorflow.org/
As for clustering, grouping not labeled data is a very interesting task because a lot of the data on the web is not labeled. For instance training model on images from video. People have to grab each image and manually label them with class or caption. This is not scalable so here unsupervised models can intervene.
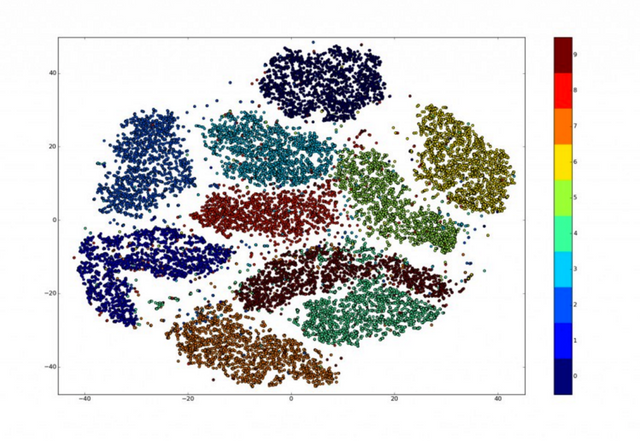
image link https://indico.io/blog/visualizing-with-t-sne/
Generative models became popular after the paper Generative Adversarial Networks, 2014. from Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and few other researchers was published. Many researchers shifted their focus to combining generative models to achieve good quality images generated from learned distributions. In the image below we can see how the generated image improves in quality training a GAN model.
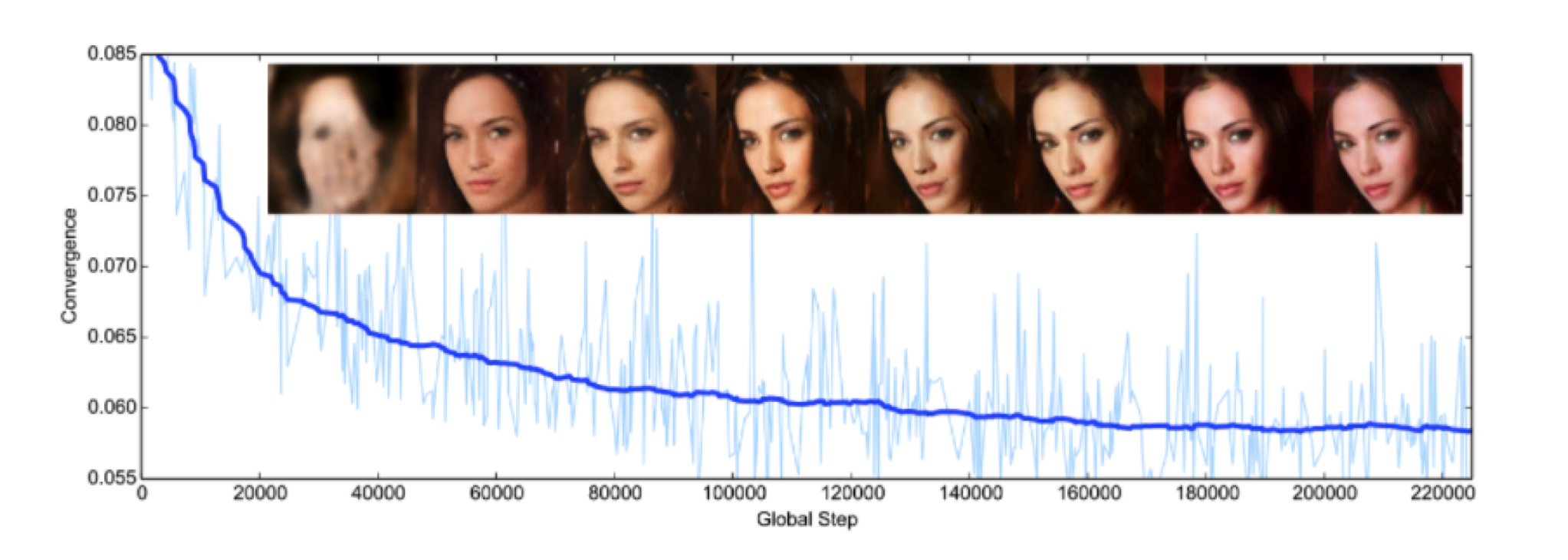
image taken from https://github.com/artcg/BEGAN
To simplify idea about unsupervised models, their goal is to extract good features that will represent a high dimensional image in lower dimensional space without having labels. Here we will present some of the most used models, auto-encoders, and generative adversarial model.
Autoencoders
An autoencoder is a neural network that is not trained classifying images into class and minimizing the error function. But it is trained to reconstruct the input image from hidden layer h. Internally, it has a hidden layer h that describes a code used to represent the input. Let’s see the image [x] below, input image enters the network, goes through layers and is being coded into hidden layer h.
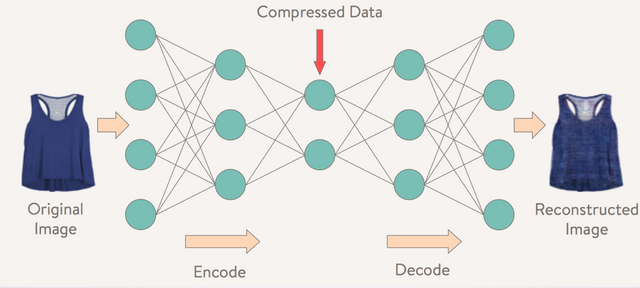
image taken from https://www.slideshare.net/TJTorres1/deep-style-using-variational-autoencoders-for-image-generation
This first part of the network is called encoder [h=f(x)]. After that, we reconstruct the image from hidden layer using the second part of the network called decoder [x’=g(h)]. The learning process is simply calculating the difference between the input image and output image. As we minimize that error our autoencoder network learns to decode high dimensional image into a good representation of the image in lower dimensional space.
Advantages of autoencoder are that it is a simple technique, reconstructing the input, layers can be stacked into stacked auto encoder and has its intuitive based on neuroscience research. But at the moment performance can’t match with supervised learning models and from some image datasets reconstruction of the input is not an ideal metric for learning a general purpose and informational representations.
Below are some links to good implementations to check out:
* https://github.com/cmgreen210/TensorFlowDeepAutoencoder
* https://github.com/musyoku/adversarial-autoencoder
Generative Adversarial models
The idea behind generative adversarial model is to have two different smaller neural network models competing. One of them called generator which takes noise as input and generates samples. The other one called discriminator, receives samples from both the generator model and the real image dataset samples. The discriminator has a goal to distinguish between generated and real samples.
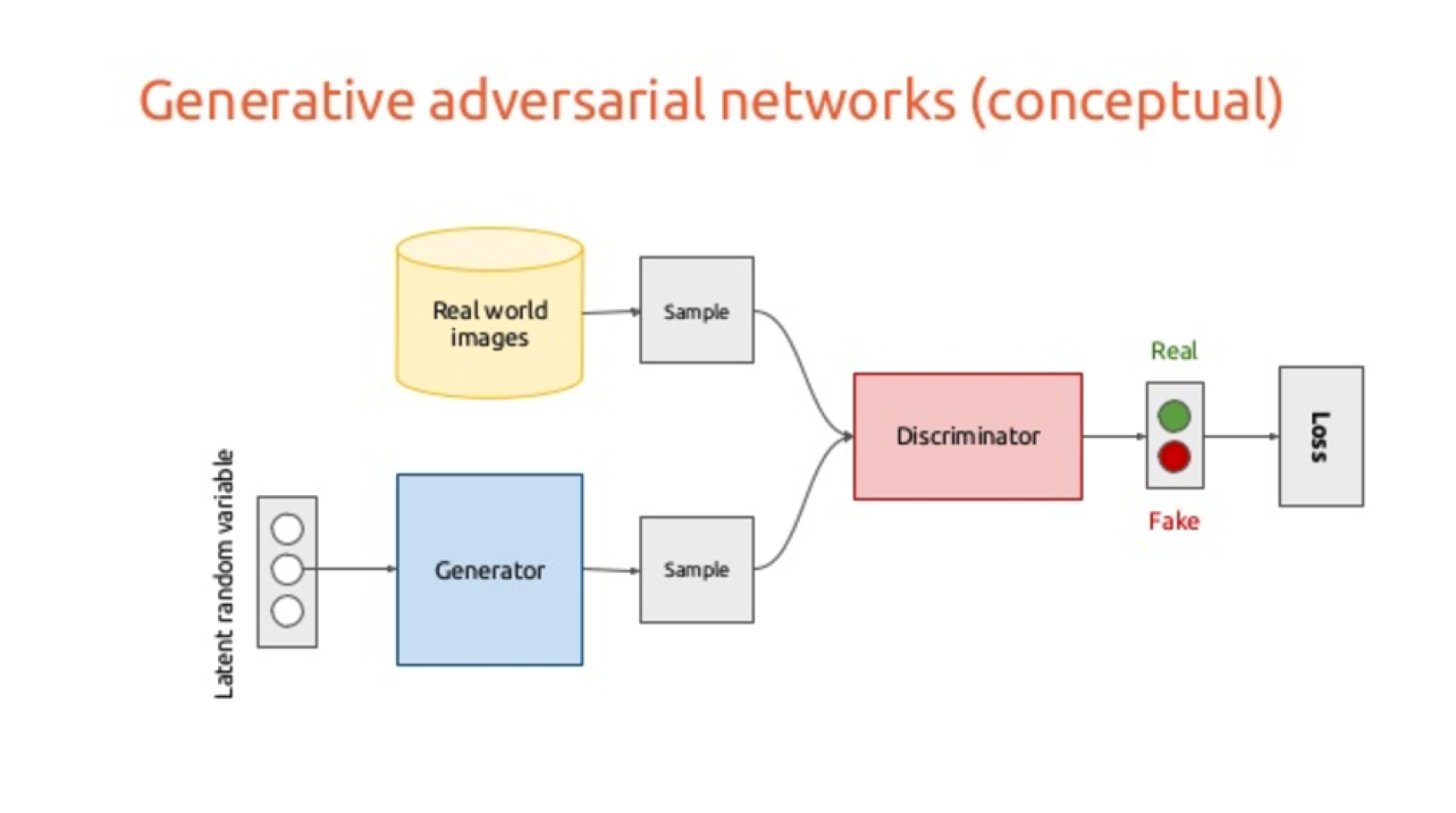
image taken from https://wiki.tum.de/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=23562510
These two networks actually have different (adversarial) roles in this continuous game. The generator is learning to produce more realistic samples to trick discriminator while discriminator becomes better and better distinguishing generated data from real. Networks are trained simultaneously and end up generating high quality images. There are many different implementations using different models, loss functions, you find a curated list of them in this link:
https://github.com/hindupuravinash/the-gan-zoo/blob/master/README.md
Below are some links to good implementations to check out:
* https://github.com/pytorch/examples/tree/master/dcgan
* https://github.com/artcg/BEGAN
* https://github.com/musyoku/wasserstein-gan
Most popular tools and libraries used in the field
* Tensorflow by Google, it is most used at the moment with huge community. There are good tutorials on https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/
* MXNET adapted by Amazon. They have huge list of models implemented in their github repository
* Torch used by Facebook. Torch is mostly used with Lua language but there is also python version PyTorch.
Useful links and materials
* Most used book in the field
http://www.deeplearningbook.org/
* Best research paper search website [Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Computer Vision]
http://www.arxiv-sanity.com/
* There are good discussions on Reddit with cited researchers adding to discussions
https://www.reddit.com/r/MachineLearning/
https://www.reddit.com/r/deeplearning/
* Search the google using [github + model] name you want to learn about, because there are plenty of implementations available to learn from
Hope you like this intro to unsupervised part of the computer vision.
Happy exploring.
extremely well made post on a topic that needs more people learning about it. AI is possibly the most important technology ever created and yet most people have no clue about how far it can really go. If you're interested in learning even more, I recommend the Two Minute Papers channel on YouTube, it's a scholarly synopsis format of over 150 papers mostly related directly to AI. Give it a look sometime.
Thank you for posting.
Yes....u r right.....You showcasing us reality...
Congratulations @eneismijmich! You have received a personal award!
Click on the badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about this award, click here
Congratulations @eneismijmich! You have received a personal award!
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
Congratulations @eneismijmich! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!