A little explanation of understanding cryptography
Cryptography (cryptography) is derived from Greek, consisting of two syllables namely crypto and grafia. Crypto means hide, while graphia means writing. Cryptography is a mathematical engineering study that deals with aspects of information security, such as data confidentiality, data validity, data integrity, and data authentication. But not all aspects of information security can be overcome with cryptography.
Cryptography can also be interpreted as a science or art to maintain the message security.
In principle, Cryptography has four main components: Plaintext, a Ciphertext readable message, a random message that can not be read Key, algorithm keys Cryptography algorithm, methods for encryption and decryption.
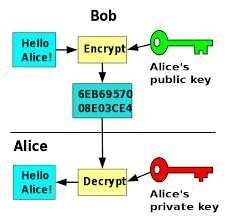
Then, the process that will be discussed in this article includes 2 basic processes in Cryptography namely: Encryption (Decryption) Decryption with the same key is used for both processes above. The use of the same key for the encryption and decryption process is also called the Secret Key, Shared Key or Symmetric Key Cryptosystem. Here is an illustration of 4 components and 2 processes used in cryptographic techniques.
Encryption
Encryption (Encryption) is the process of making plaintext messages into random messages that can not be read (ciphertext). Here is an example of the encryption used by Julius Caesar, by replacing each letter with the next 3 letters (also called Additive / Substitution Cipher).
Plaintext
home
Motorcycle
stove
Ciphertext
xasgn
suzux
qusvux
DecryptionDescription is a reverse encryption process where this process will convert ciphertext into plaintext by using 'inverting' and the same key algorithm. Example:
Ciphertext
xasgn
suzux
qusvux
Plaintext
home
Motorcycle
stove
Source
http://asalkena.blogspot.com/2012/11/pengertian-and-contoh.html