The Steemit Crypto Academy Week 1 : Blockchain and Blockchain Consensus Mechanism
I'm glad to join this new innovation by @steemitblog to sensitize new crypto users, improve the knowledge of old crypto users and also to broaden our scope about cryptocurrencies.
I will be dropping my first assignment given by @gbenga who is the chosen @cryptoacademy professor for Nigeria. This is my first post in 2021 so I'll love to say Happy New Year to all Steemians.
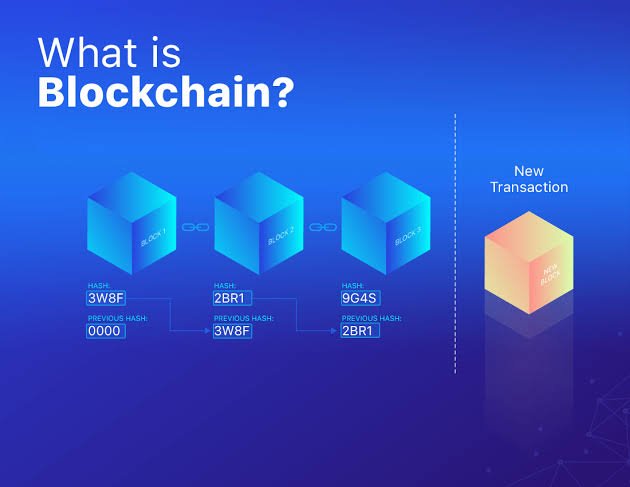
Image downloaded from (https://google.com)
WHAT IS BLOCK CHAIN?
To the best of my knowledge, Blockchain is a system of recording information in a way that makes it difficult or impossible to change, hack, or cheat the system.
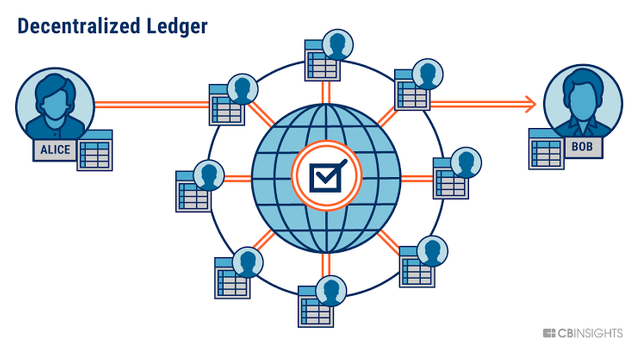
Image downloaded from (https://google.com)
A blockchain is essentially a digital ledger of transactions that is duplicated and distributed across the entire network of computer systems on the blockchain. Each block in the chain contains a number of transactions, and every time a new transaction occurs on the blockchain, a record of that transaction is added to every participant’s ledger. The decentralised database managed by multiple participants is known as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT).
Blockchain is a type of DLT in which transactions are recorded with an immutable cryptographic signature called a hash.
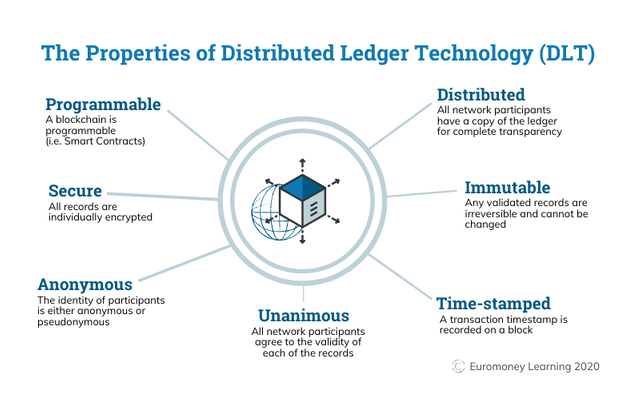
Image downloaded from (https://www.euromoney.com)
This means if one block in one chain was changed, it would be immediately apparent it had been tampered with. If hackers wanted to corrupt a blockchain system, they would have to change every block in the chain, across all of the distributed versions of the chain.
Blockchains such as Bitcoin and Ethereum are constantly and continually growing as blocks are being added to the chain, which significantly adds to the security of the ledger. Blockchain, which began to emerge as a real-world tech option in 2016 and 2017, is poised to change IT in much the same way open-source software did a quarter century ago.
- In Simple terms,
Based on a peer-to-peer (P2P) topology, blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that allows data to be stored globally on thousands of servers – while letting anyone on the network see everyone else's entries in near real-time. That makes it difficult for one user to gain control of, or game, the network.
BLOCKCHAIN MECHANISM
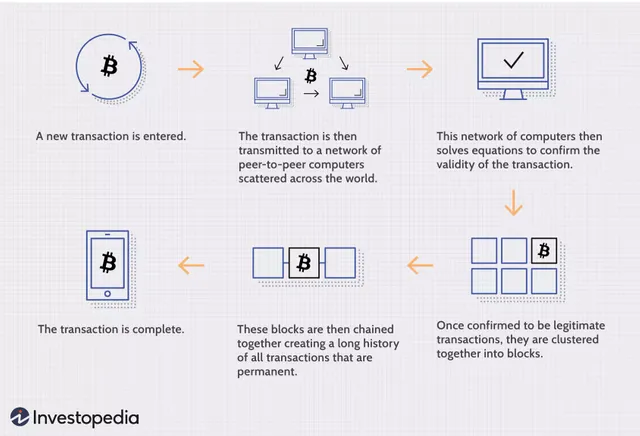
Image downloaded from (https://google.com)
The term "Blockchain" came into existence sometime in 2008. When Bitcoin Blockchain was first created. The term bitcoin was first coined in 2008 when Satoshi Nakamoto wrote a paper about a "peer-to-peer version of electronic cash that would allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution."
For the purpose of understanding blockchain, it is instructive to view it in the context of how it has been implemented by Bitcoin. Like a database, Bitcoin needs a collection of computers to store its blockchain. For Bitcoin, this blockchain is just a specific type of database that stores every Bitcoin transaction ever made. In Bitcoin’s case, and unlike most databases, these computers are not all under one roof, and each computer or group of computers is operated by a unique individual or group of individuals.
.jpeg)
Image downloaded from (https://google.com)
In a blockchain, each node has a full record of the data that has been stored on the blockchain since its inception. For Bitcoin, the data is the entire history of all Bitcoin transactions. If one node has an error in its data it can use the thousands of other nodes as a reference point to correct itself. This way, no one node within the network can alter information held within it. Because of this, the history of transactions in each block that make up Bitcoin’s blockchain is irreversible.
.jpeg)
Image downloaded from (https://google.com)
If one user tampers with Bitcoin’s record of transactions, all other nodes would cross-reference each other and easily pinpoint the node with the incorrect information. This system helps to establish an exact and transparent order of events. For Bitcoin, this information is a list of transactions, but it is also possible for a blockchain to hold a variety of information like legal contracts, state identifications, or a company’s product inventory.
NOTE:
Blockchain can only be updated by consensus between participants in the system, and once new data is entered it can never be erased. It is a write-once, append-many technology, making it a verifiable and auditable record of each and every transaction.
HOW HAS BLOCKCHAIN AFFECT FINANCE?
.jpeg)
Image downloaded from (https://google.com)
The blockchain, as a form of distributed ledger technology (DLT), has transformed well-established financial institutions and bring lower costs, faster execution of transactions, improved transparency, auditability of operations, and other benefits.
Elimination of intermediaries in market structures. Unlike the physical markets, where there are retailers who adds to the prices of goods and commodities, Blockchain has been able to eradicate the actions of middlemen as a user or trader can directly access the blockchain on his own.
Blockchain has improved financial services as it has given more room for crypto users to trade in large volume of cryptocurrencies and the identity of the trader becomes safe.
Blockchain has also affected our day-to-day operations. It has reduced drastically the danger in moving about with large amount of money for physical trading which is definitely less secured. All transactions are done online and cashless policy is encouraged.
Thanks for coming along with me in my first assignment. Follow my blog @akeenze11 to read more about my future posts on Blockchain and it's effects on Financial technology.
Very good post mr Akeenze11
Besides i am the boy you invited to steemit at your mum's place