SLC | S21W3 || Costs for entrepreneurs - Costing methods
Assalam-o-Alaikum! |
|---|


What are costing methods and what is their importance? |
|---|
Costing procedures are techniques used to determine how much it costs to produce a good or provide a service. Businesses may see the costs of each step in the production process by breaking costs down into categories such as labor, materials and other charges. For instance every step in the chair making process, such as wood cutting, assembly and painting has a cost. Understanding these specifics aids in determining areas for cost savings and setting reasonable prices. Different business types benefit from different costing techniques such as job costing or process costing. The price of ingredients, preparation and delivery are all determined independently for a breakfast delivery service.
The company is able to determine where to invest and where to make cuts if necessary because they can see exactly how much they spend on each service.The proper costing technique is essential for maintaining firm profitability as it expands. Understanding individual costs helps a business avoid unforeseen costs and maintain fair prices for customers as it grows. Businesses can also modify pricing in response to market shifts thanks to clear costing which keeps them profitable while maintaining their competitiveness.
Explain the difference between the job order and process costing methods. |
|---|
Here I want to explain few differences between Job Order Costing and Process Costing .
| Job Order Costing | Process Costing |
|---|---|
| Used when products or services are unique or customized. | Used when identical products are mass-produced. |
| Costs are tracked per individual job or order. | Costs are tracked by each stage or process. |
| Works well for small batches or one-time projects. | Works well for large-scale, continuous production. |
| Example: Custom furniture or tailored clothing. | Example: Beverage production or paper manufacturing. |
| Detailed tracking is required for each specific order. | Tracking is done for each production process as a whole. |
| Cost calculation can vary from one job to another. | Cost per unit is uniform across all products. |
| Direct labor and materials vary by order specifications. | Labor and materials are consistent across all items. |
| Overhead is assigned to individual jobs separately. | Overhead is spread evenly across production processes. |
| Ideal for businesses with custom or complex products. | Ideal for companies that make similar items in bulk. |
| Focuses on cost control per order to ensure profitability. | Focuses on cost efficiency in each production process. |
Research and explain, to the best of your understanding, two costing methods different from those explained in this class. |
|---|

Standard costing on the other hand establishes a standard cost for every product by using projected prices for labor, materials and overhead. This benchmark is used by businesses to plan and regulate spending, and any discrepancies are then compared to real costs. This approach is helpful for efficiency measurement and budgeting. When real expenses vary It assists the business in identifying problems and making changes for upcoming production based on typical expenses.
Perform the costing by work orders, according to what was explained for a cake manufacturing business
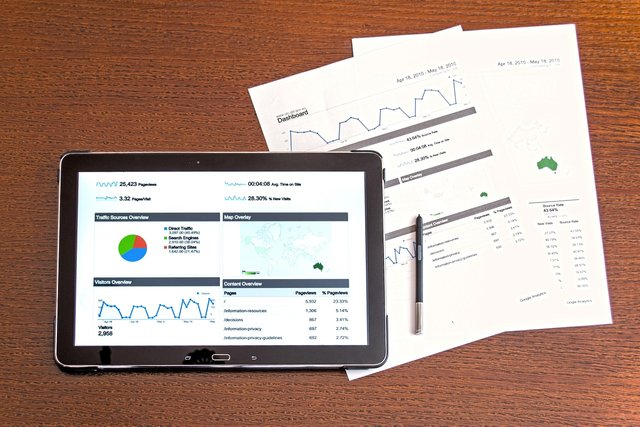

This makes it easier to monitor the precise labor costs for every unique cake and guarantees equitable pricing according to labor and time. Lastly we include indirect manufacturing costs for each cake, such as electricity equipment wear and oven maintenance. We might allocate $2 in electricity for each cake order if there are 50 cakes produced and the monthly electricity cost is $100. We can set pricing that cover all costs and maintain business profitability by using this breakdown to assess the whole cost each order.
I want to explain supposing cost order for a cake making business. If a cake calls for particular raw materials . So
Direct Raw Materials (DRM) As an illustration let say that flour is $5, sugar is $3 and eggs are $2. The total DRM for this cake is equal to flour plus sugar and eggs.

Direct Labor (DLM) The labor cost is determined by the baker hourly wage and the amount of time required. For instance a baker hourly rate is $10 and it takes two hours to prepare one cake. The total DLM for this cake is equal to the hourly rate times the number of hours worked.

IPCs or indirect production costs Indirect expenses such as power, are distributed among all cakes made in a given month. For instance:cake = Monthly Power Expense / Total Cakes Made -$100 divided by 50 is $2**

IPC per cakeTotal Cost = DRM + DLM + IPC so Total Cost per Cake Order$10 + $20 + $2 = $32 is the total cost. Therefore the entire cost of making this specific cake would be $32.

I invite @shano49 @malikusman1 and @saboohi to take participate in this contest

Thank you

https://steemit.com/hive-172186/@neelofar/achievement1-my-introduction-to-steemit
WRITER:
@neelofar from Pakistan

@neelofar from Pakistan


Greetings @neelofar
1.- You have explained very well the definition of costing methods, explaining some of them highlighting their importance, emphasizing that they are a set of specific procedures used to determine a cost.
2.- You have explained some of the aspects that differentiate job order costing and process costing, indicating the specific differences in them and how both are linked to the way of production.
3.- You have explained two other types of costing such as activity-based costing and standard costing, indicating their main characteristics and how their implementation is useful. .
4.- You have provided the cost calculation of the production of cakes, according to the work order method. The calculations made are in accordance with what was explained in class.
Thanks for joining the contest