强化学习—— Q-Learning 玩 MountainCar 爬坡上山

Image from unsplash.com by Brandon Wallace
之前的文章结合理论和实践熟悉了 Q-Learning 的经典算法,这篇文章我们基于 Open AI 的经典 MountainCar 环境。用 python 代码实现 Q-Learning 算法,完成小车爬坡上山的挑战。
同样的,为了方便与读者交流,所有的代码都放在了这里:
https://github.com/zht007/tensorflow-practice
1. Gym 环境初始化
要熟悉 MountainCar-v0 的环境请参见官网以及官方的 github repo.
MountainCar-v0 的环境状态是由 其位置和速度决定的。行为 Action 有三个,向左 (0),向右 (2),无(1) 推车。奖励: 除了超过目的地 (位置为 0.5), 其余地方的奖励均为 "-1"
初始化 gym 环境的代码如下
env = gym.make("MountainCar-v0")
env.reset
当然强化学习中的参数不要忘了初始化
LEARNING_RATE = 0.5
DISCOUNT = 0.95
EPISODES = 10000
SHOW_EVERY = 500
Code from Github Repo with MIT lisence
2. Q-Table 的建立
Q表是用来指导每个状态的行动,由于该环境状态是连续的,我们需要将连续的状态分割成若干个离散的状态。状态的个数即为 Q 表的size。这里我们将Q表长度设为20,建立一个 20 x 20 x 3 的Q表。
DISCRETE_OS_SIZE = [Q_TABLE_LEN] * len(env.observation_space.high)
discrete_os_win_size = (env.observation_space.high - env.observation_space.low) / DISCRETE_OS_SIZE
q_table = np.random.uniform(low=0, high=1,
size=(DISCRETE_OS_SIZE + [env.action_space.n]))
Code from Github Repo with MIT lisence
另外,我们采用 epsilon-greedy 的策略,epsilon 采用衰减的方式,一开始为1最后衰减为0,也就是说智能体一开始勇敢探索,接下来贪婪行动获取最大奖励。
epsilon = 1 # not a constant, qoing to be decayed
START_EPSILON_DECAYING = 1
END_EPSILON_DECAYING = EPISODES//2
epsilon_decay_value = epsilon/(END_EPSILON_DECAYING - START_EPSILON_DECAYING)
Code from Github Repo with MIT lisence
3. 帮助函数
将环境"离散"化,以适应离散的Q表
def get_discrete_state (state):
discrete_state = (state - env.observation_space.low) // discrete_os_win_size
return tuple(discrete_state.astype(int))
epsilon-greedy 策略帮助函数
def take_epilon_greedy_action(state, epsilon):
discrete_state = get_discrete_state(state)
if np.random.random() < epsilon:
action = np.random.randint(0,env.action_space.n)
else:
action = np.argmax(q_table[discrete_state])
return action
Code from Github Repo with MIT lisence
4. 训练智能体
Q-learning属于单步Temporal Difference (时间差分TD(0))算法,其通用的更新公式为
其中 td_target - Q[s,a] 部分又叫做 TD Error.
Q-learning:
核心代码如下:
for episode in range(EPISODES):
# initiate reward every episode
ep_reward = 0
state = env.reset()
done = False
while not done:
action = take_epilon_greedy_action(state, epsilon)
next_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
ep_reward += reward
if not done:
td_target = reward + DISCOUNT * np.max(q_table[get_discrete_state(next_state)])
q_table[get_discrete_state(state)][action] += LEARNING_RATE * (td_target - q_table[get_discrete_state(state)][action])
elif next_state[0] >= 0.5:
# print("I made it on episode: {} Reward: {}".format(episode,reward))
q_table[get_discrete_state(state)][action] = 0
state = next_state
Code from Github Repo with MIT lisence
5 查看训练效果
我们训练了 10000 次,将每500次的平均奖励,最大奖励,最小奖励结果画出来如下:
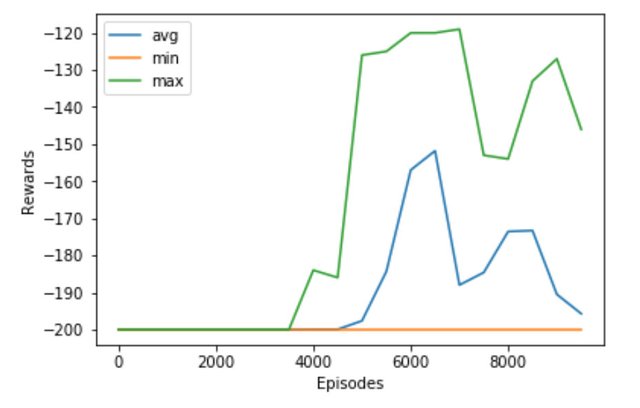
可见,从大慨3000个回合的时候,智能体开始学会如何爬上山顶。
当然最直观的查看训练效果都方法即将动画render 出来,根据Q表来Render 动画的代码如下:
done = False
state = env.reset()
while not done:
action = np.argmax(q_table[get_discrete_state(state)])
next_state, _, done, _ = env.step(action)
state = next_state
env.render()
env.close()
动画如下:
6. 总结
Q - learning 的关键在于如何建立Q-表,特别是处理环境状态为连续的情况,当然我们还会遇到行动空间同样为连续的情况,这种情况该如何处理呢?我们将在后面的文章介绍。
参考资料
[1] Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction (2nd Edition)
[2] David Silver's Reinforcement Learning Course (UCL, 2015)
[3] Github repo: Reinforcement Learning
相关文章
AI学习笔记——动态规划(Dynamic Programming)解决MDP(1)
AI学习笔记——动态规划(Dynamic Programming)解决MDP(2)
AI学习笔记——MDP(Markov Decision Processes马可夫决策过程)简介
吃了吗?你好!家中可愛的寵物照想要跟大家分享嗎?或是出去玩拍到一些可愛的動物,別忘了到@dpet分享,可以得到@dpet的獎勵喔!倘若你想让我隐形,请回复“取消”。
This post has been voted on by the SteemSTEM curation team and voting trail. It is elligible for support from @curie.
If you appreciate the work we are doing, then consider supporting our witness stem.witness. Additional witness support to the curie witness would be appreciated as well.
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!
Please consider setting @steemstem as a beneficiary to your post to get a stronger support.
Please consider using the steemstem.io app to get a stronger support.