用 Keras 轻松搭建模型实现DQN
前面已经有好几篇文章介绍了DQN的理论了,这里就不在赘述了,直接用 Keras 进行项目实战。
源代码请查看我的repo
https://github.com/zht007/tensorflow-practice
1. 环境参数设定
gym 的环境参数设定与 Q-learning 类似,我们这里用 MountainCar 环境为例。在DQN中需要设定的是用于记忆回放的 replay_memory,以及其大小 REPLAY_MEMORY_SIZE。MIN_REPLAY_MEMORY_SIZE 是最小回放长度,只有超过这个长度,才开始回放并训练。
ACTION_SPACE_SIZE = env.action_space.n
REPLAY_MEMORY_SIZE = 50_000
MIN_REPLAY_MEMORY_SIZE = 1_000
MINIBATCH_SIZE = 64
UPDATE_TARGET_EVERY = 5
DISCOUNT = 0.99
EPISODES =1000
同样的这里设定了一个随 episode 下降的 epsilon.
# Exploration settings
epsilon = 1 # not a constant, going to be decayed
EPSILON_DECAY = 0.995
MIN_EPSILON = 0.001
ep_rewards = []
AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY = 50
MIN_EPSILON = 0.001
Code from github repo with MIT license
2. 建立网络模型
用 Keras 建立神经网络模型,与监督学习中用到的网络类似,可以是全连接的,也可以是CNN 或者 RNN。这里我们用的是三层全连接的网络结构。
这里要注意的是输入输出的 shape ,由于第一层输入的是 states 所以要与 observation_space 的 shape 一致。输出的是 action, 所以输出的shape 要与 action space 一致。
def create_model(self):
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(Dense(16 ,input_shape=(env.observation_space.shape)))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(Dense(16))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(Dense(16))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(Dense(ACTION_SPACE_SIZE))
model.add(Activation('linear'))
print(model.summary())
model.compile(loss = 'mse', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001),metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
3. DQN 智能体
这里需要用到面向对象的编程方法,建立智能体这个类(Class).
3.1 智能体类变量
智能体有 4 个 类变量:
用于回放的记忆库 replay_memory
Prediction 网络模型: model_prediction
Target 网络模型: model_target
用于记录回放次数的计数器:target_update_counter
在DQN中有两个神经网络,一个相对固定 Target Model,一个用于训练即 Prediction Model,所以两者网络结构一模一样。用 create_model 方法创建即可。
Prediction Model 会定期将参数复制给 Target Model,而这个target_update_counter就是用来判定是否到了该传参数的时候。
class DQNAgent:
def __init__(self):
# Replay memory
self.replay_memory = deque(maxlen=REPLAY_MEMORY_SIZE)
# Prediction Network (the main Model)
self.model_prediction = create_model()
# Target Network
self.model_target = create_model()
self.model_target.set_weights(self.model_prediction.get_weights())
# Used to count when to update target network with prediction network's weights
self.target_update_counter = 0
3.2 获取q值,更新replay_memory
两个方法都属于类方法,获取q值即用神经网络 Predict Action 的 Q值
def get_qs(self, state):
return self.model_prediction.predict(np.array(state).reshape(-1, *state.shape))[0]
更新reply_memory 即将当前的 sate, action, next_sate, done 四个信息存入记忆体中,用于之后的回放训练。
# (state, action, reward, next_state, done)
def update_replay_memory(self, transition):
self.replay_memory.append(transition)
3.3 训练神经网络
训练神经网络首先要搞清楚是训练哪一个神经网络,model_target 是不需要训练的,其参数是定期从 model_prediction 获取的。需要不停地被训练的是 model_prediction。
其次,要搞清楚训练的 “Feature” 和 “Label” 即 X 和 y 是什么。
X 是 states,
y 类似 Q-learning 中的 td_target
Q-Learning回顾
Q[s, a]+= learning_rate } ( td_target -Q[s, a])
其中:
td_target =R[t+1] + discout_factormax(Q[s'])
s‘代表下一个状态
对于 DQN states 是从记忆库(replay_memory[s, a, s' done] )中提取出来的, a 和 s' 也是从记忆库中提取出来的。于是可以通过 Model Prediction 和 s 得到 prediction 的 q 表, 通过 s‘ 和 Model Target 得到 target 的 q 表,并求出其中最大的 q_max。最后将这个 q_max 送到 Model Prediction 通过反向传播更新 Model。整个过程如下图所示。
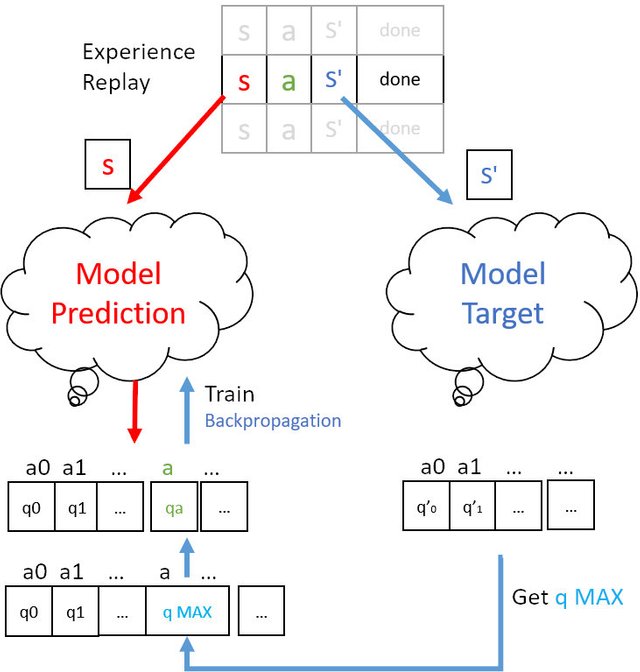
Image created by @hongtao
补充两点,记忆回放是以mini batch 的形式在replay_memory 中随机抽取的。Model_target 的参数定期更新,该部分完整代码如下
def train(self, terminal_state, step):
if len(self.replay_memory) < MIN_REPLAY_MEMORY_SIZE:
return
minibatch = random.sample(self.replay_memory, MINIBATCH_SIZE)
# Get current states from minibatch, then query NN model_prediction for current Q values
current_states = np.array([transition[0] for transition in minibatch])
current_qs_list = self.model_prediction.predict(current_states)
# Get next_states from minibatch, then query NN model_target for target Q values
# When using target network, query it, otherwise main network should be queried
next_states = np.array([transition[3] for transition in minibatch])
target_qs_list = self.model_target.predict(next_states)
X = []
y = []
# Now we need to enumerate our batches
for index, (current_state, action, reward, next_state, done) in enumerate(minibatch):
# If not a terminal state, get new q from future states, otherwise set it to 0
# almost like with Q Learning, but we use just part of equation here
if not done:
max_target_q = np.max(target_qs_list[index])
new_q = reward + DISCOUNT * max_target_q
else:
new_q = reward
# Update Q value for given state
current_qs = current_qs_list[index]
current_qs[action] = new_q
# And append to our training data
X.append(current_state)
y.append(current_qs)
# Fit on all samples as one batch, log only on terminal state
self.model_prediction.fit(np.array(X), np.array(y), batch_size=MINIBATCH_SIZE, verbose=0, shuffle=False if terminal_state else None)
# Update target network counter every episode
if terminal_state:
self.target_update_counter +=1
# If counter reaches set value, update target network with weights of main network
if self.target_update_counter > UPDATE_TARGET_EVERY:
self.model_target.set_weights(self.model_prediction.get_weights())
self.target_update_counter = 0
Code from github repo with MIT license
4. 创建并训练智能体
该部分也与Q-learning 十分相似。
第一步:Epsilon Greedy 的策略判断是采取随机行动还是用模型 model_prediction 预测行动。
第二步:采取行动,并将(s, a, s' done) 放入记忆库
第三步:训练模型 model_prediction
该部分代码如下:
agent = DQNAgent()
# Iterate over episodes
for episode in tqdm(range(1, EPISODES + 1), ascii=True, unit='episodes'):
# # Update tensorboard step every episode
# agent.tensorboard.step = episode
# Restarting episode - reset episode reward and step number
episode_reward = 0
step = 1
# Reset environment and get initial state
current_state = env.reset()
# Reset flag and start iterating until episode ends
done = False
while not done:
# This part stays mostly the same, the change is to query a model for Q values
if np.random.random() > epsilon:
# Get action from Q table
action = np.argmax(agent.get_qs(current_state))
else:
# Get random action
action = np.random.randint(0, ACTION_SPACE_SIZE)
next_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
# Transform new continous state to new discrete state and count reward
episode_reward += reward
# if SHOW_PREVIEW and not episode % AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY:
# env.render()
# Every step we update replay memory and train main network
agent.update_replay_memory((current_state, action, reward, next_state, done))
agent.train(done, step)
current_state = next_state
step += 1
# Append episode reward to a list and log stats (every given number of episodes)
ep_rewards.append(episode_reward)
if not episode % AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY or episode == 1:
average_reward = sum(ep_rewards[-AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY:])/len(ep_rewards[-AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY:])
min_reward = min(ep_rewards[-AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY:])
max_reward = max(ep_rewards[-AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY:])
# rewards recording
aggr_ep_rewards['ep'].append(episode)
aggr_ep_rewards['avg'].append(average_reward)
aggr_ep_rewards['min'].append(min_reward)
aggr_ep_rewards['max'].append(max_reward)
# Decay epsilon
if epsilon > MIN_EPSILON:
epsilon *= EPSILON_DECAY
epsilon = max(MIN_EPSILON, epsilon)
Code from github repo with MIT license
5. 查看训练效果
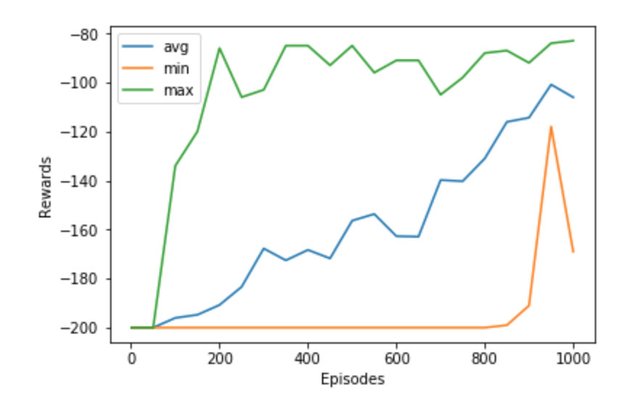
可以看到在大概200 个回合的时候最大奖励的曲线已经操过-90, 平均奖励的曲线也一直在稳步上升。
最后,可以查看动画,可以看到小车非常轻松地就爬上了山顶。
done = False
state = env.reset()
while not done:
qs_list = agent.get_qs(state)
action = np.argmax(qs_list())
next_state, _, done, _ = env.step(action)
state = next_state
env.render()
env.close()
参考资料
[1] Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction (2nd Edition)
[2] David Silver's Reinforcement Learning Course (UCL, 2015)
[3] Github repo: Reinforcement Learning
相关文章
强化学习——Q-Learning SARSA 玩CarPole经典游戏
AI学习笔记——动态规划(Dynamic Programming)解决MDP(1)
AI学习笔记——动态规划(Dynamic Programming)解决MDP(2)
AI学习笔记——MDP(Markov Decision Processes马可夫决策过程)简介
你那里天气如何?欢迎在steemauto里设置跟赞 @cnbuddy 给整个cn区点赞如果不想再收到我的留言,请回复“取消”。
This post has been voted on by the SteemSTEM curation team and voting trail. It is elligible for support from @curie.
If you appreciate the work we are doing, then consider supporting our witness stem.witness. Additional witness support to the curie witness would be appreciated as well.
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!
Please consider setting @steemstem as a beneficiary to your post to get a stronger support.
Please consider using the steemstem.io app to get a stronger support.