the greenhouse effect
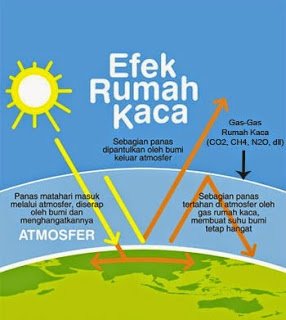
Burning petroleum, coal and forest fires either because human actions or occur naturally leads to an increase in carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere. This gas is also produced from various combustion. The more burning, the more carbon oxide. Then the carbon in the oxide will be caulked in the earth's atmosphere. The greenhouse effect can increase global temperatures so that climate patterns change around the world. When this event occurs, the resulting effect can melt the polar ice. When the ice melts the meal the sea level will rise. This situation affects the ecological balance thus endangering the lives of humans and other living beings.
When the atmosphere is rich with greenhouse gases, it is increasingly becoming an insulator that holds better, both the heat from the sun that is emitted to the earth. Currently, the atmosphere contains a major component of greenhouse gases, ie CO2, of as much as 380 ppm (380 molecules per million molecules). Before the industrial revolution took place, the amount of CO2 was 275 ppm. In order for the earth's temperature not to rise to 2 0C, atmospheric CO2 levels must be below 450 ppm.
In essence, the earth heats up because the heat of the sun can not go out again so that the glass gases of the house to enlarge the atmosphere that can split the sun rays. Certainly rising temperatures in the northern regions of the northern hemisphere will heat up more than other areas of the earth. As a result the icebergs will melt and the datas will shrink. The average surface temperature of the earth is about 15 C (F59). During the last hundred years, the average temperature has increased by 0.6 degrees Celsius (1 degree Fahrenheit). The scientists estimate further warming so that 1, h4 - 5.8 degrees Celsius (2.5 - 10.4 degrees Fahrenheit) in 2010.