Blockchain — a revolutionary technology — simply explained
During the development of the crypto currency “Bitcoin”, a technology was created whose potential BlockHealth wants to use for a substantial change in the accessibility, documentation and provision of its own health data — the so-called “Blockchain technology”, in which several encryption techniques are linked together.
Similar to the Internet itself, which was originally developed by CERN scientists for the exchange of knowledge, the Blockchain technology opens up possibilities that go far beyond the originally intended use.

What is Blockchain?
“Blockchain” is a digital, decentralized database in which various encryption techniques are combined to significantly increase protection against data theft and manipulation.
In other words, a blockchain is a constantly expandable series of data sets, the so-called “blocks”, which are linked together using cryptographic methods. Each data record (“block”) consists of many individual transactions, encrypted information about the previous block and a time stamp.
On the one hand, the decentralized structure ensures a high degree of security, since the respective data is no longer collected in a central location, on the other hand, direct contact without an intermediary is possible.
In addition to increasing efficiency by eliminating an intermediary, manipulation of the data stored by blockchain technology is almost impossible.
How does Blockchain-Technology work?
If a transaction is executed in a blockchain, the details are as follows:
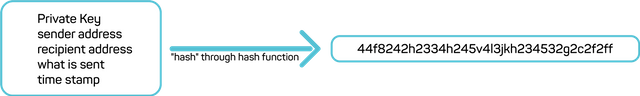
Each transaction contains the “private key” (secret code, password) of the person executing the transaction.
This private key is combined with the sender address, the recipient address, individually defined information (money, contract, findings, prescription,…) and a time stamp.
This information is now reduced to a certain number of numbers and letters by a “hash function”, a special algorithm. The combination of numbers and letters, also called hash, is the transaction ID, which contains all the necessary information of the transaction in encrypted form.
A transaction must either be complete and error-free or not executed at all.
If the transaction is correct, the transaction ID lands in the current block. As soon as a certain amount of transaction IDs is available, i.e. the block has reached a certain memory size, the entire block is again hashed into a certain combination of numbers and letters. The new combination of numbers and letters, therefore, contains all the information of the entire block and is at the same time the beginning of a new “block” to which the next transaction IDs are now added.
Note: This is a very simplified representation and should only explain the principle!
In short: each block contains the information of the previous block.
If you tried to change a transaction or information in a transaction afterwards, the combination of numbers and letters (the transaction ID) would change immediately, which in turn would change the entire block ID. As a result, this block would no longer correlate with all other blocks and the block chain would “break”, so to speak.
Therefore, it is almost impossible to manipulate the existence or content of previous transactions unnoticed without simultaneously destroying all subsequent transactions that were confirmed by the previous ones.
Since all participants of the decentralized blockchain network, the so-called “Miner” (proof of work) or “Witnesses” (proof of stake), have knowledge of all transactions and blocks, they would simply recognize a manipulated copy of the blockchain by the fact that it is much shorter than their own or has inconsistencies in the evidence.
Application examples
The following paragraphs list some interesting applications of blockchain technology
Concluding smart contracts using Blockchain technology
One of the best-known applications of the Blockchain are “Smart Contracts”. Smart Contracts are web-based computer protocols that map contracts and technically implement the processing of a contract. A smart contract also determines which conditions lead to which decision. Thus, contracts can also be concluded without a legal entity, as these algorithms monitor contracts in real time and automatically enforce the rights of the respective party. For example, if a customer does not pay the monthly instalment for his car after the third reminder, the vehicle no longer drives off.
Smart contracts are therefore algorithms that map contracts that automatically recognize whether the contract conditions are being adhered to.
Blockchain to improve value chains
Blockchain technology has the potential to simplify entire value chains, make them transparent and thus safer. In this way, every single step that a product has taken within a supply chain could be recorded.
This ensures, for example, that frozen food has been properly transported and stored and that the cold chain has not been interrupted.
In addition, the place of origin of products can also be verified, which above all guarantees consumers greater transparency with regard to the place of origin of their goods.
The blockchain makes it possible to trace the path a product has taken until it finally gets into one’s own hands, from which region it comes and whether child labor was used.
This technology is particularly interesting in the food and dietary supplement sector or in the field of pharmacology in order to create more transparency.
Revolution in Electric Mobility with Blockchain Technology
Another interesting possibility to use blockchain technology lies in the following scenario:
Charging electric cars without stationary charging — in future, electric cars could be charged by induction while the car is at a red light, for example. The small sums of money for the electricity are then paid by means of microtransactions via the Blockchain technology.
In addition to using blockchain in the field of currency, there are many other ways in which this revolutionary technology can be used.