Is blockchain technology the new internet?
The blockchain is an undeniably ingenious invention – the brainchild of a person or group of people known by the pseudonym, Satoshi Nakamoto. But since then, it has evolved into something greater, and the main question every single person is asking is: What is Blockchain?By allowing digital information to be distributed but not copied, blockchain technology created the backbone of a new type of internet. Originally devised for the digital currency, Bitcoin, (Buy Bitcoin) the tech community is now finding other potential uses for the technology.Bitcoin has been called “digital gold,” and for a good reason. To date, the total value of the currency is close to $9 billion US. And blockchains can make other types of digital value. Like the internet (or your car), you don’t need to know how the blockchain works to use it. However, having a basic knowledge of this new technology shows why it’s considered revolutionary. So, we hope you enjoy this, what is Blockchain guide.
What is Blockchain Technology?
“The blockchain is an incorruptible digital ledger of economic transactions that can be programmed to record not just financial transactions but virtually everything of value.”
Don & Alex Tapscott, authors Blockchain Revolution (2016)
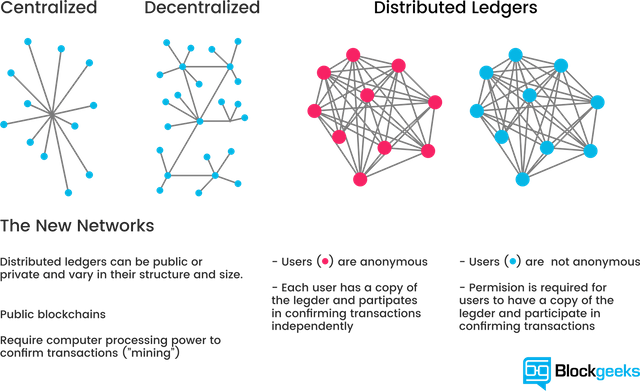
A distributed database
Picture a spreadsheet that is duplicated thousands of times across a network of computers. Then imagine that this network is designed to regularly update this spreadsheet and you have a basic understanding of the blockchain.
Information held on a blockchain exists as a shared — and continually reconciled — database. This is a way of using the network that has obvious benefits. The blockchain database isn’t stored in any single location, meaning the records it keeps are truly public and easily verifiable. No centralized version of this information exists for a hacker to corrupt. Hosted by millions of computers simultaneously, its data is accessible to anyone on the internet.To go in deeper with the Google spreadsheet analogy, I would like you to read this piece from a blockchain specialist.
Blockchain as Google Docs
“The traditional way of sharing documents with collaboration is to send a Microsoft Word document to another recipient, and ask them to make revisions to it. The problem with that scenario is that you need to wait until receiving a return copy before you can see or make other changes because you are locked out of editing it until the other person is done with it. That’s how databases work today. Two owners can’t be messing with the same record at once.That’s how banks maintain money balances and transfers; they briefly lock access (or decrease the balance) while they make a transfer, then update the other side, then re-open access (or update again).With Google Docs (or Google Sheets), both parties have access to the same document at the same time, and the single version of that document is always visible to both of them. It is like a shared ledger, but it is a shared document. The distributed part comes into play when sharing involves a number of people.Imagine the number of legal documents that should be used that way. Instead of passing them to each other, losing track of versions, and not being in sync with the other version, why can’t *all* business documents become shared instead of transferred back and forth? So many types of legal contracts would be ideal for that kind of workflow.You don’t need a blockchain to share documents, but the shared documents analogy is a powerful one.”William Mougayar, Venture advisor, 4x entrepreneur, marketer, strategist and blockchain specialist
Blockchain Durability and robustness
Blockchain technology is like the internet in that it has a built-in robustness. By storing blocks of information that are identical across its network, the blockchain cannot:
- Be controlled by any single entity.
- Has no single point of failure.
Bitcoin was invented in 2008. Since that time, the Bitcoin blockchain has operated without significant disruption. (To date, any of problems associated with Bitcoin have been due to hacking or mismanagement. In other words, these problems come from bad intention and human error, not flaws in the underlying concepts.)The internet itself has proven to be durable for almost 30 years. It’s a track record that bodes well for blockchain technology as it continues to be developed.
“As revolutionary as it sounds, Blockchain truly is a mechanism to bring everyone to the highest degree of accountability. No more missed transactions, human or machine errors, or even an exchange that was not done with the consent of the parties involved. Above anything else, the most critical area where Blockchain helps is to guarantee the validity of a transaction by recording it not only on a main register but a connected distributed system of registers, all of which are connected through a secure validation mechanism.” – Ian Khan, TEDx Speaker | Author | Technology Futurist
Transparent and incorruptible
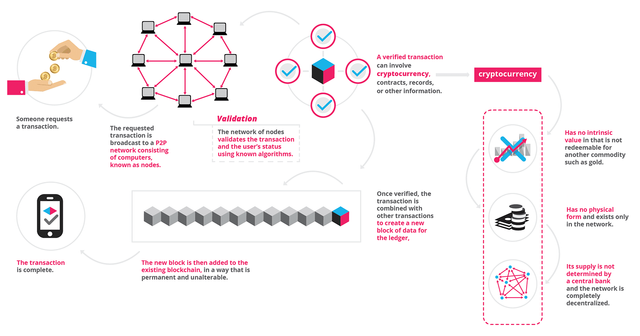
The blockchain network lives in a state of consensus, one that automatically checks in with itself every ten minutes. A kind of self-auditing ecosystem of a digital value, the network reconciles every transaction that happens in ten-minute intervals. Each group of these transactions is referred to as a “block”. Two important properties result from this:
- Transparency data is embedded within the network as a whole, by definition it is public.
- It cannot be corrupted altering any unit of information on the blockchain would mean using a huge amount of computing power to override the entire network.
In theory, this could be possible. In practice, it’s unlikely to happen. Taking control of the system to capture Bitcoins, for instance, would also have the effect of destroying their value.“Blockchain solves the problem of manipulation. When I speak about it in the West, people say they trust Google, Facebook, or their banks. But the rest of the world doesn’t trust organizations and corporations that much — I mean Africa, India, the Eastern Europe, or Russia. It’s not about the places where people are really rich. Blockchain’s opportunities are the highest in the countries that haven’t reached that level yet.”
Vitalik Buterin, inventor of Ethereum
A network of nodes
A network of so-called computing “nodes” make up the blockchain.
Node
(computer connected to the blockchain network using a client that performs the task of validating and relaying transactions) gets a copy of the blockchain, which gets downloaded automatically upon joining the blockchain network. Together they create a powerful second-level network, a wholly different vision for how the internet can function.Every node is an “administrator” of the blockchain, and joins the network voluntarily (in this sense, the network is decentralized). However, each one has an incentive for participating in the network: the chance of winning Bitcoins.Nodes are said to be “mining” Bitcoin, but the term is something of a misnomer. In fact, each one is competing to win Bitcoins by solving computational puzzles. Bitcoin was the raison d’etre of the blockchain as it was originally conceived. It’s now recognized to be only the first of many potential applications of the technology.There are an estimated 700 Bitcoin-like cryptocurrencies (exchangeable value tokens) already available. As well, a range of other potential adaptations of the original blockchain concept are currently active, or in development.
“Bitcoin has the same character a fax machine had. A single fax machine is a doorstop. The world where everyone has a fax machine is an immensely valuable thing.”
Larry Summers, Former US Secretary of the Treasury
The idea of decentralization
By design, the blockchain is a decentralized technology.Anything that happens on it is a function of the network as a whole. Some important implications stem from this. By creating a new way to verify transactions aspects of traditional commerce could become unnecessary. Stock market trades become almost simultaneous on the blockchain, for instance — or it could make types of record keeping, like a land registry, fully public. And decentralization is already a reality.A global network of computers uses blockchain technology to jointly manage the database that records Bitcoin transactions. That is, Bitcoin is managed by its network, and not any one central authority. Decentralization means the network operates on a user-to-user (or peer-to-peer) basis. The forms of mass collaboration this makes possible are just beginning to be investigated.
Who will use the blockchain?
“I think decentralized networks will be the next huge wave in technology.”
Melanie Swan, author Blockchain: Blueprint for a New Economy (2015)
As web infrastructure, you don’t need to know about the blockchain for it to be useful in your life.Currently, finance offers the strongest use cases for the technology. International remittances, for instance. The World Bank estimates that over $430 billion US in money transfers were sent in 2015. And at the moment there is a high demand for blockchain developers.The blockchain potentially cuts out the middleman for these types of transactions. Personal computing became accessible to the general public with the invention of the Graphical User Interface (GUI), which took the form of a “desktop”. Similarly, the most common GUI devised for the blockchain are the so-called “wallet” applications, which people use to buy things with Bitcoin, and store it along with other cryptocurrencies.Transactions online are closely connected to the processes of identity verification. It is easy to imagine that wallet apps will transform in the coming years to include other types of identity management.
The Blockchain & Enhanced security
“Online identity and reputation will be decentralized. We will own the data that belongs to us.”
William Mougayar, author The Business Blockchain: Promise, Practice, and Application of the Next Internet Technology (2016)
“Online identity and reputation will be decentralized. We will own the data that belongs to us.”
William Mougayar, author The Business Blockchain: Promise, Practice, and Application of the Next Internet Technology (2016)