Has WannaCry malware just returned?

Cyber crime related to cryptocurrency is increasing, the latest hacker attack was directed against the Bithumb cryptocurrencies exchange and caused the damage of more than $30 million. Recently, the UK's National Fraud and Cyber Crime Reporting Centre, Action Fraud, has warned of a new form of scam consisting in sending emails to the victims who are informed that their devices were infected by WannaCry ransom ware.
By the end of last week, Action Fraud had received over 300 reports of people receiving phishing emails with information about alleged malware that infected their computers. The person behind he emails assured that the user's electronic devices had been hacked and the data would be deleted unless the user paid Bitcoins as ransom. In fact, those emails were designed to cause public panic and trick the victims into believing that their computers were infected with the WannaCry malware.
In May 2017, the attack of the WannaCry malware affected 200,000 victims and more than 300,000 computers, causing millions of dollars in damage . Even the NHS (National Health Service) and many other international organizations were affected by the virus.
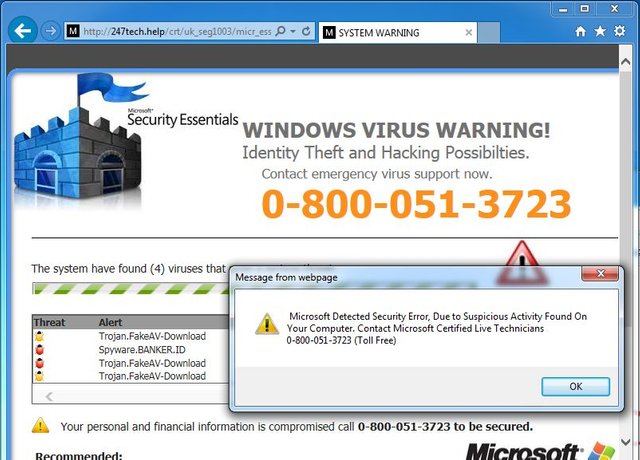
This is not the first time hackers have taken advantage of WannaCry to scam people. In 2017, Action Fraud received many alerts from computer users that they received various pop-ups announcing that their computers had been infected with WannaCry. The recipients of the message were then asked to call the attached phone numbers in order to contact tech supporters at Microsoft or Apple.
The methods often used by hackers are easily recognizable and predictable as the majority of their attacks are carried out in a similar way. Several types of emails should get our attention, especially ones that are sent with the information that a computer malfunction has been detected and we are asked to fix it; emails with unauthorized 'software upgrades'; those that require credit card information to verify the Windows version or announce that we won the Microsoft Lottery.
Computer and cyber security firms recommend that users should delete those emails immediately and be extremely careful when someone asks them to provide credit card information or personal information to prevent the risk of losing money and to protect themselves from identity theft, as Microsoft does not require a credit card to validate the Windows version.
In addition, let’s remember that most pop-up ads are unreliable, and in order to increase our cybersecurity we should not answer phone calls from strange phone numbers, , allow remote connection on personal electronic devices and most importantly never share passwords or personal information with strangers.
Written by @daigv from nami.today
To the question in your title, my Magic 8-Ball says:
Hi! I'm a bot, and this answer was posted automatically. Check this post out for more information.