3-Tier Architecture
The Three Tiers in a 3-Tier Architecture
Presentation Tier
The presentation tier occupies the top level of the application. It sends content to browsers in the web development frameworks, such as CSS, HTML, or JavaScript, and displays information in the form of a graphical user interface (GUI), which allows users to can access directly. It communicates with other layers by putting out the results to the browser and other tiers through API calls.
Application Tier
The application tier is also called the business logic, logic tier, or middle tier. By processing the business logic for the application, it builds a bridge between the presentation layer and the data layer to make communication faster between the presentation and data layer.
The application tier is usually coded in C#, Java, C++, Python, Ruby, etc.
Data Tier
Data-tier is composed of persistent storage mechanism and the data access layer. It supports connecting with the database and to perform insert, update, delete, get data from the database based on our input data.
Rules in the 3-Tier Architecture
The core rule: the presentation layer is only a shell and cannot contain any processing of BizLogic.
The design should from the application layer rather than the presentation layer. And the API of the application layer should implement all BizLogic on the API in an object-oriented manner.
Whether the data layer is a simple SqlHelper or a class with Mapping, make sure it is independent of the abstract system layer.
Whether you’re using COM+(EnterpriseService), Remoting, or a remote object technology like WebService, whether you’re deploying it on a server or not, you have to consider clustering multiple servers through load balancing in your design
To sum up, when considering whether a project conforms to the application of a three-tier or multi-tier design, it is necessary to find whether it conforms to the requirements of the project.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a 3-Tier Architecture?
Advantages:
- It reduces dependencies between layers. Therefore, As long as follow the interface standards and use the same entity classes of the object model, it allows different developers to work on each layer, which can significantly improve the development speed of the system.
- Each layer can be redeveloped or modernized without affecting other layers in a 3-tier architecture. Therefore, shortens time to market and reduces the cost to integrate new features into software as a service (SaaS), Cloud, and on-premise applications.
- It provides ease of maintenance, won’t affect other modules, which dramatically reduces maintenance costs and maintenance time.
- Instead of directly accessing the data layer, the presentation layer only connects with the business logic layer, which improves data security.
Disadvantages:
- It reduces system performance. Without a hierarchical structure, the businesses could go directly to the database to get the data, but now they have to go through the middle tier.
- The 3-tier architecture sometimes results in cascading changes, especially happens in the top-down direction. If you need to add a feature in the presentation layer, you may need to add code in both the business logic layer and the data access layer to ensure that the design is layered.
3-Tier Architecture Example
Take FineReport as an example to help you better understand the 3-tier architecture. FineReport is reporting software adopted the 3-tier architecture.
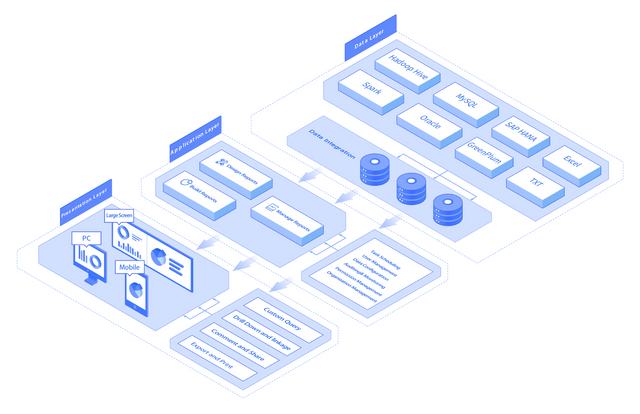
The data layer of FineReport is responsible for data management, including data collection, ETL, building a data warehouse, etc. It supports multiple data sources and data integration.
The application layer of FineReport is responsible for the main functions and business logic. In this part, as an enterprise reporting tool, it supports reports design, reports generation, and reports management.
In the presentation layer, FineReport can adaptively display reports and dashboards on the PC, mobile, and TV screens because the charts in FineReport are developed by HTML5, which can be used cross-platform, adaptive to web design, and support instant update.
For example, when you want to create a sales report based on the sales data stored in the CRM, the presentation layers send API calls to the data layer, the data layer of the FineReport runs the query and returns the results to the application layer, which formats it into a web page. The page is then sent back to the browser, where the presentation layer displays the reports on a laptop or other device.
With the 3-tier architecture, you only need to install the designer on the report designer’s computer, and then deploy the project to the server. Other users can directly access the report as long as there is a browser on the computer.
Once the report requirements change, it is very convenient to design locally and then publish to the remote server by switching the working directory or directly edit the report files on the remote server.
In this way, for companies, it only needs to deploy the project once, and then it can be designed directly and remotely, which makes migrating reports conveniently and improves efficiency.
Original Source:https://www.finereport.com/en/product-functions/3-tier-architecture.html