SLC S23 Week4 || Quadrilaterals
Hello everyone! I hope you will be good. Today I am here to participate in the contest of @sergeyk about Quadrilaterals. It is really an interesting and knowledgeable contest. There is a lot to explore. If you want to join then:

Build a parallelogram, demonstrate its elements and properties.
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and equal to each other. The opposite angles are also equal.
In the geogebra I have built Parallelogram by using the following procedure:
- Took two points A and B.
- Connected two points with segment.
- I placed the 3rd point C by using the parallel line tool by selecting the side AB. This point is not on the side AB.
- I connected the point C with A with a segment.
- Then I used parallel line tool again and I selected the line AC and passed through a parallel line to it passing from the point B.
- The intersection of these two parallel lines gave me an intersection point which is the fourth vertex D.
- I used segment tool to draw all the sides and hide the parallel lines.
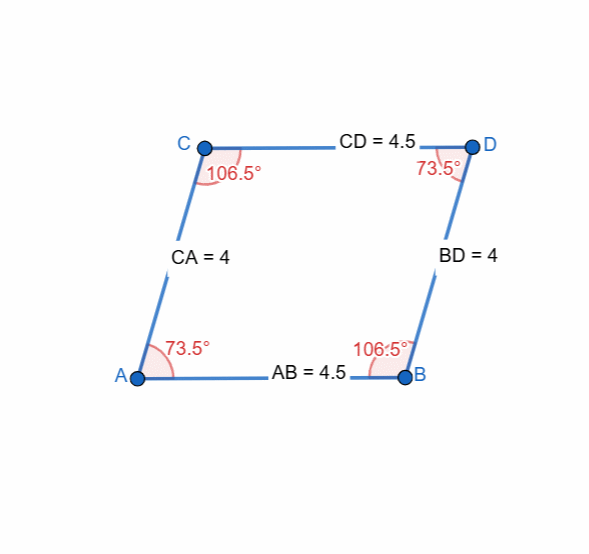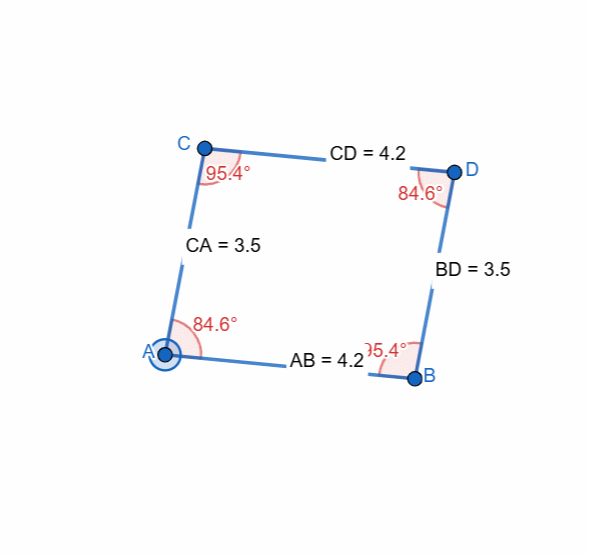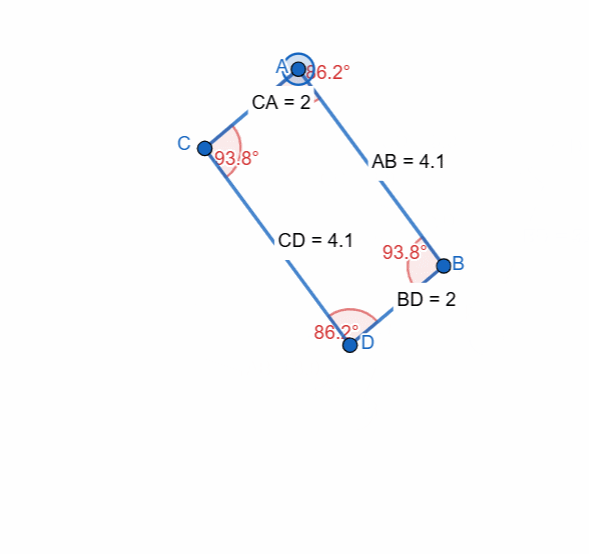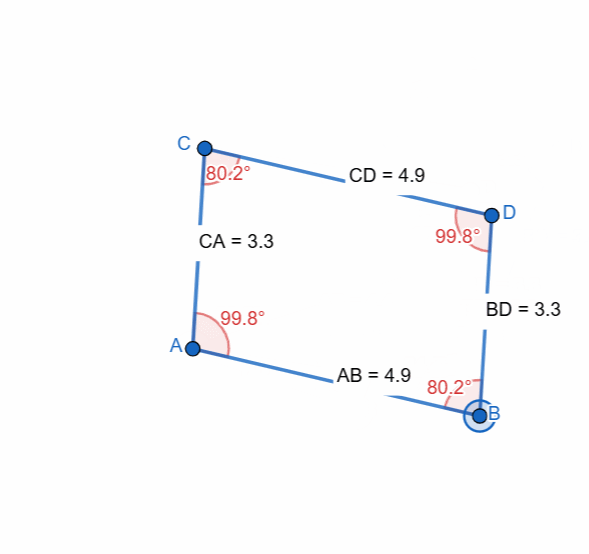
Elements and Properties of Parallelogram
Here are all the elements and properties of the parallelogram:
- It has four vertices.
- It has four sides.
- The sum of all the internal angles is always 360.
- The length of the opposite sides is equal and the opposite sides are equal.
- The diagonals bisect each other.
- The diagonals have mid points at the same point. At their mid points they intersect each other.
- It has two pairs of opposite angles.
- The opposite angles are equal.
- Each diagonal divides the parallelogram into two congruent triangles.
- The adjacent angles are supplementary.
- Area of Parallelogram = Base×Height
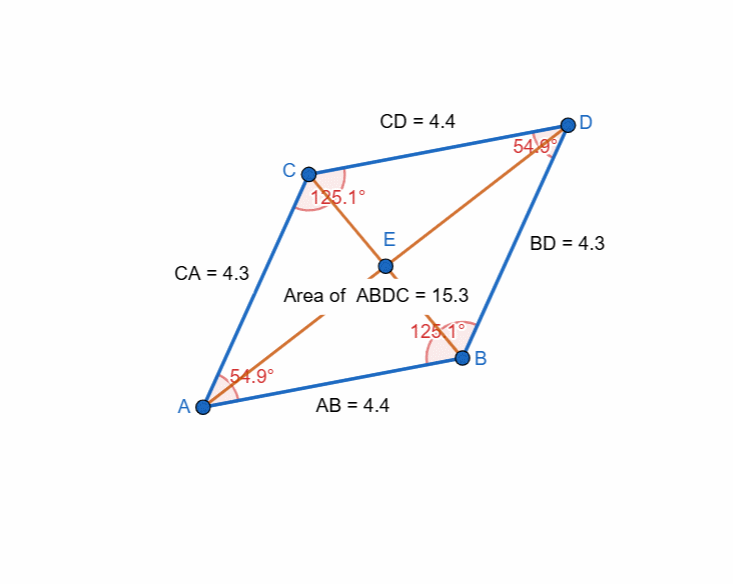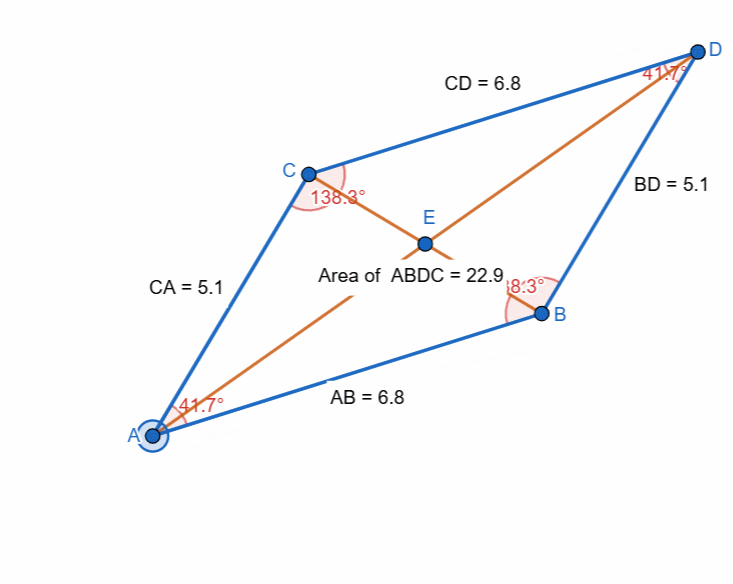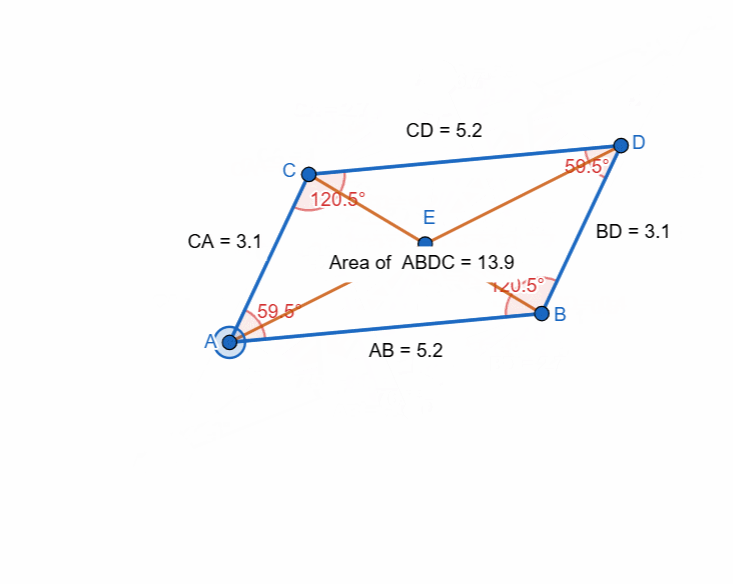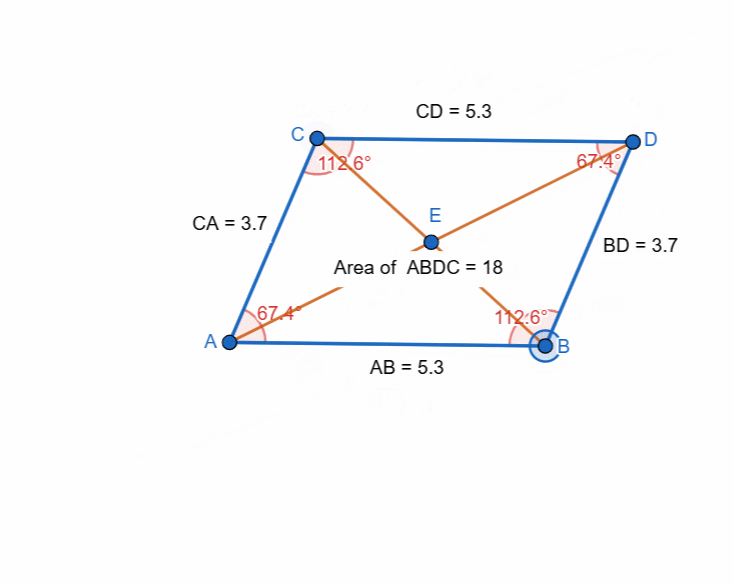
Here I have tried to show all the properties of the parallelogram and it can be seen that as the shape is changing itself the values are also changing and most importantly the opposite sides and the angles have equal value all the time.
Build a trapezoid, demonstrate its elements and properties.
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides. It is also known as a trapezium.
In the geogebra I have built trapezoid by using the following procedure:
- I placed three points A, B, and D.
- I connected the points and in this way two sides of the trapezoid were ready.
- I drew a parallel line to the side AD passing through the point B.
- I took a point C on the parallel line.
- I connected the point C to the point D with segment and similar used segment to make the side BC.
- I hide the parallel line.
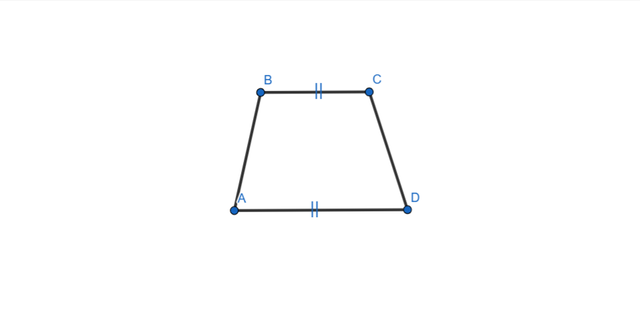
Elements and Properties of Trapezoid
Here are all the elements and properties of the trapezoid:
- It has four vertices.
- It has four sides.
- Two sides are the bases. AD is lower base and BC is higher base.
- Two sides are non-parallel here AB and CD.
- The perpendicular height between two bases is the altitude or the height of the trapezoid.
- The line segments which join the opposite corners are the diagonals of the trapezoid.
- Each trapezoid has midsegment which is the line joining the mid points of the legs.
- The mid segment is equal to the average of the bases.
- Midsegment = (Base1 + Base2)/2
- Sum of all the angles is 360.
- Adjacent angles along non-parallel sides are supplementary.
- Area of Trapezoid = 1/2 (Base1 + Base2) x Height
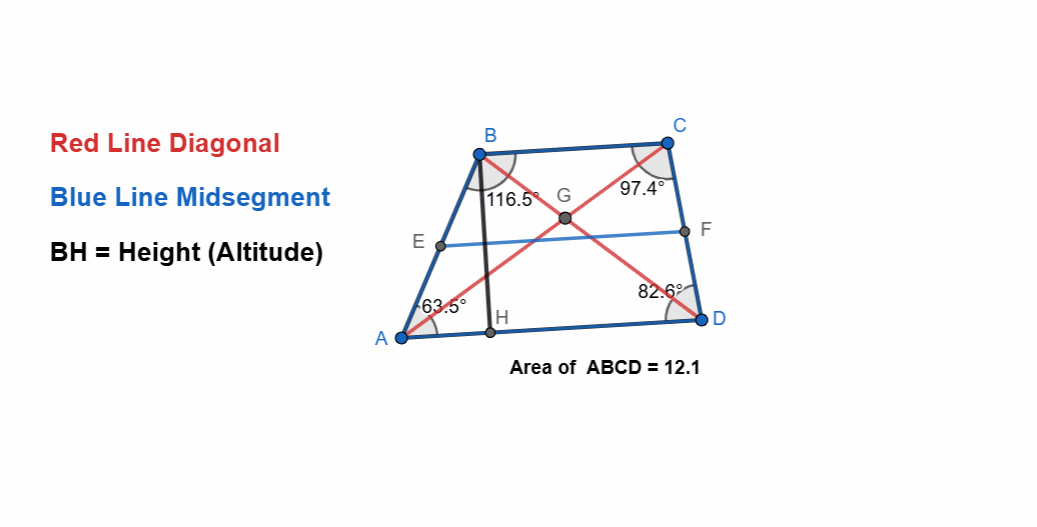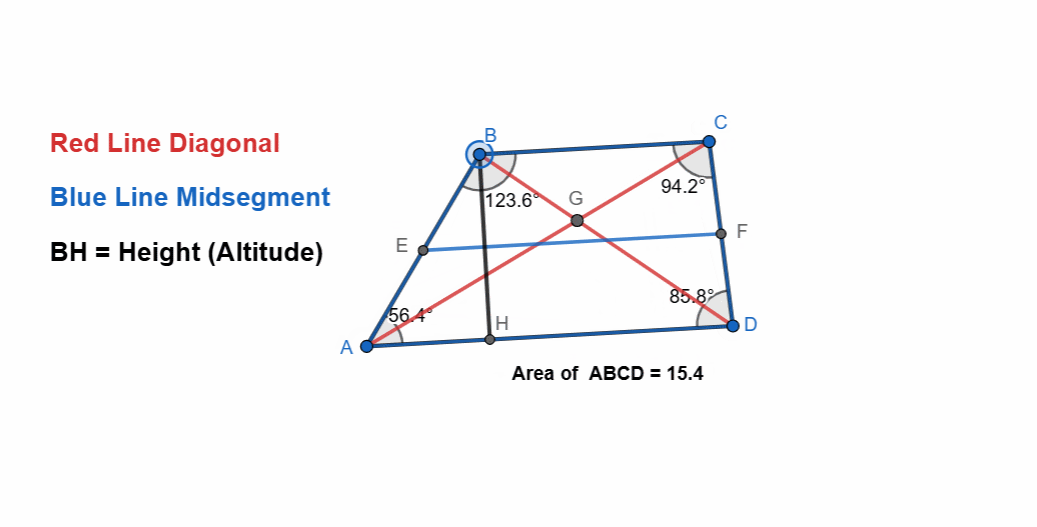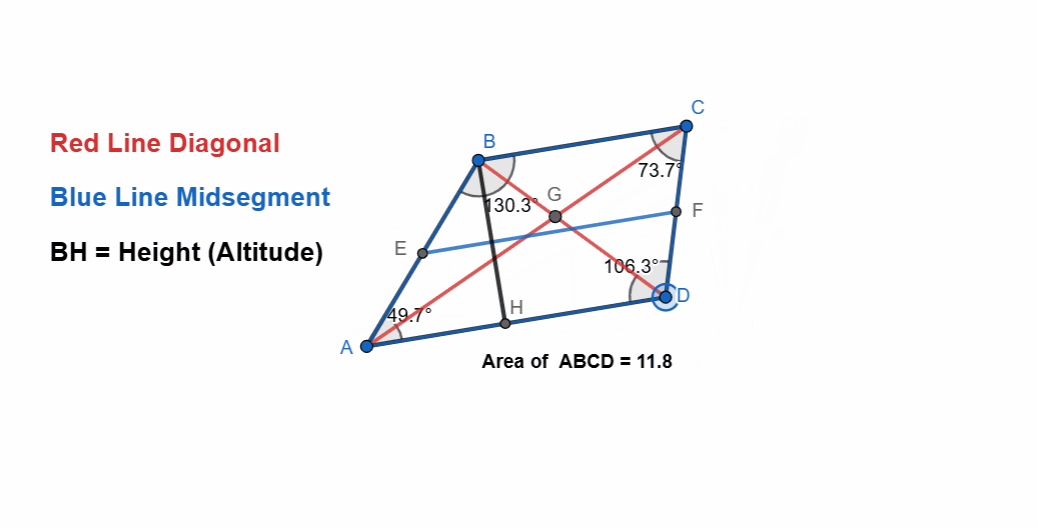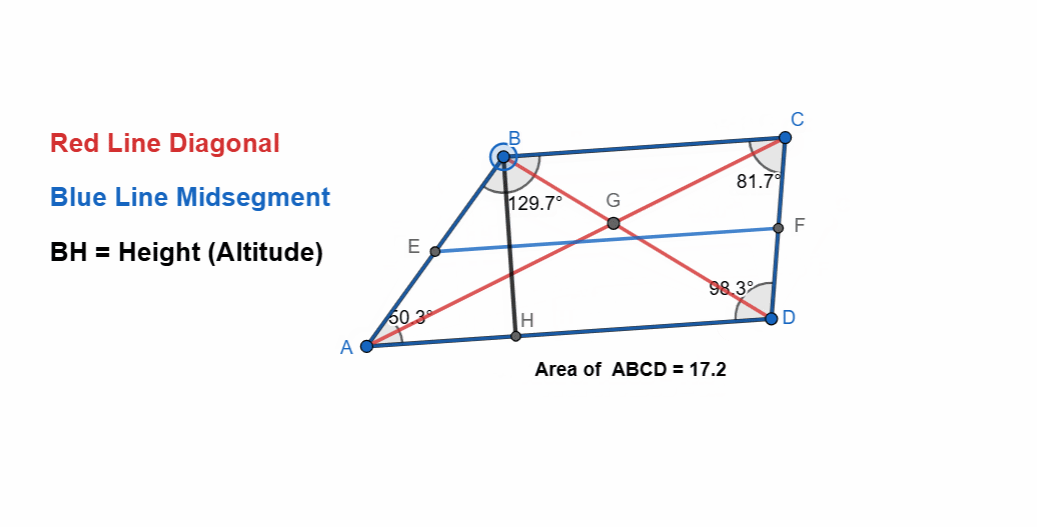
Here I have tried to show all the properties of the trapezoid and it can be seen that as the shape is changing itself the values are also changing. The adjacent angles are supplementary and the sum of all angles is 360. The two sides are parallel to each other.
Right Trapezoid
A right trapezoid is a trapezoid which has at least one right angle. It is very simple to create a right trapezoid.
- I took a segment AB.
- I created a vertical line passing through point A and similarly from B by using perpendicular line tool.
- I took point C randomly at vertical line passing through A.
- I took point D at vertical line passing through B but this point was at different height.
- I connected all points with polygon tool and right trapezoid formed.
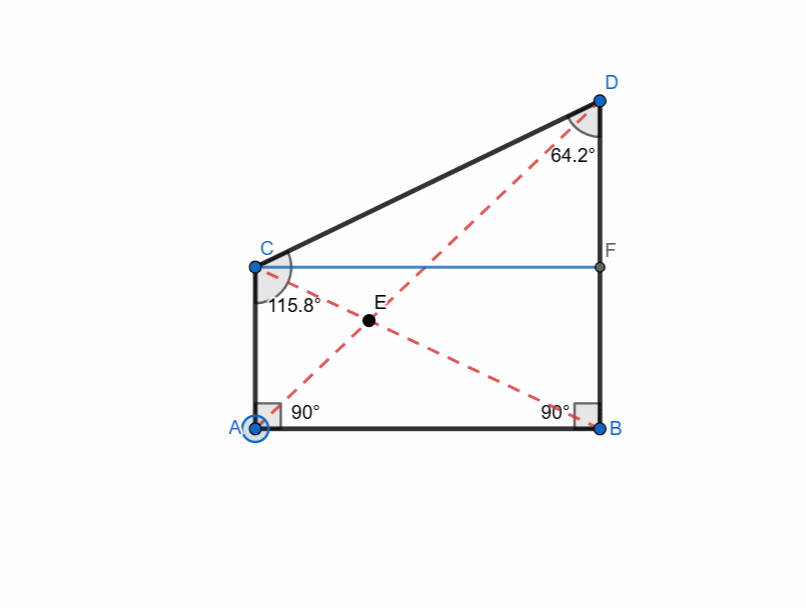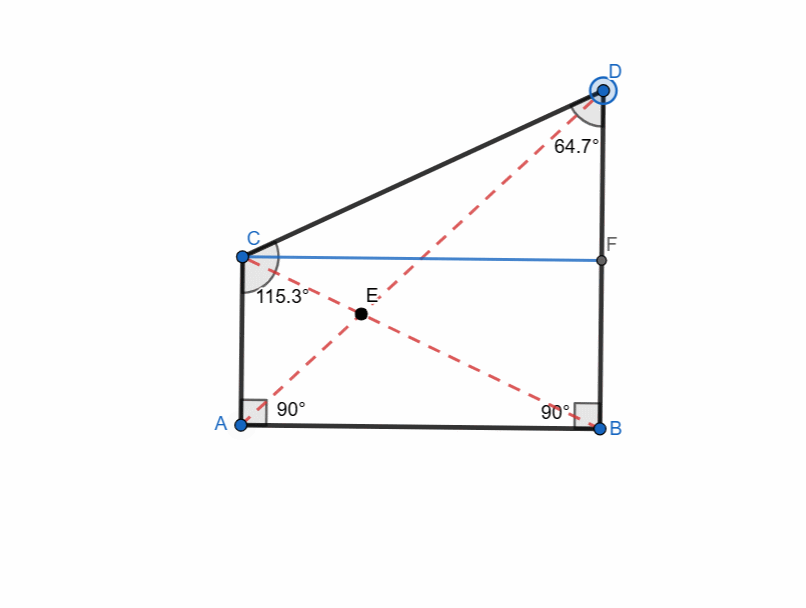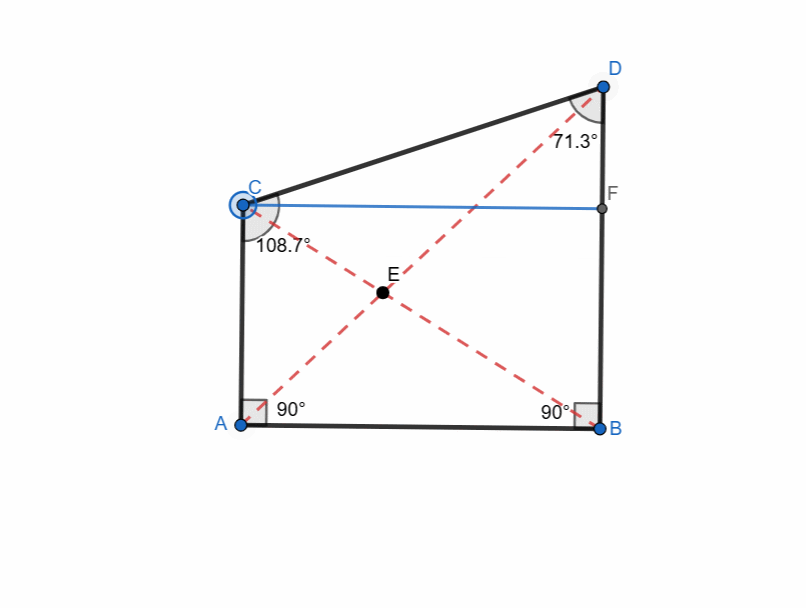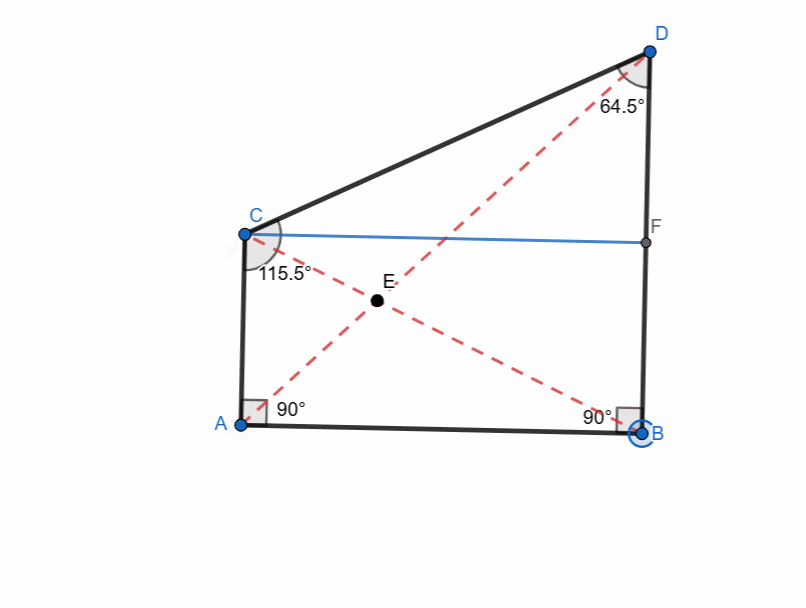
It has following properties:
- One pair of parallel sides.
- Two right angles.
- Non-parallel sides can be of different lengths.
- Perpendicular distance between the parallel bases is height.
- Diagonals are not equal in length.
A stair step or the is often in the shape of a right trapezoid.
Isosceles Trapezoid
A right trapezoid is a trapezoid which has equal non-parallel sides and equal angles at bases. It is very simple to create an isosceles trapezoid.
- I took a base with segment as AB.
- I found the midpoint.
- I drew the height with perpendicular passing through midpoint.
- I took a point C on this line passing through midpoint.
- I drew a parallel line to AB passing through D.
- Then I placed a point E on this line.
- Then I used reflect object on a line tool to place a symmetric point on the other side.
- I connected all the points with segment.
- Isosceles trapezoid formed.
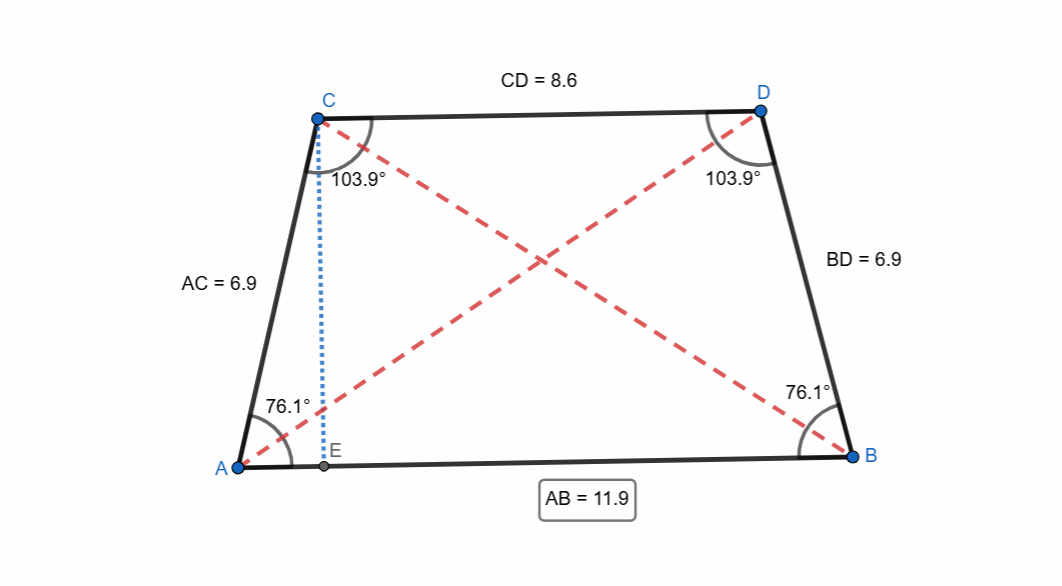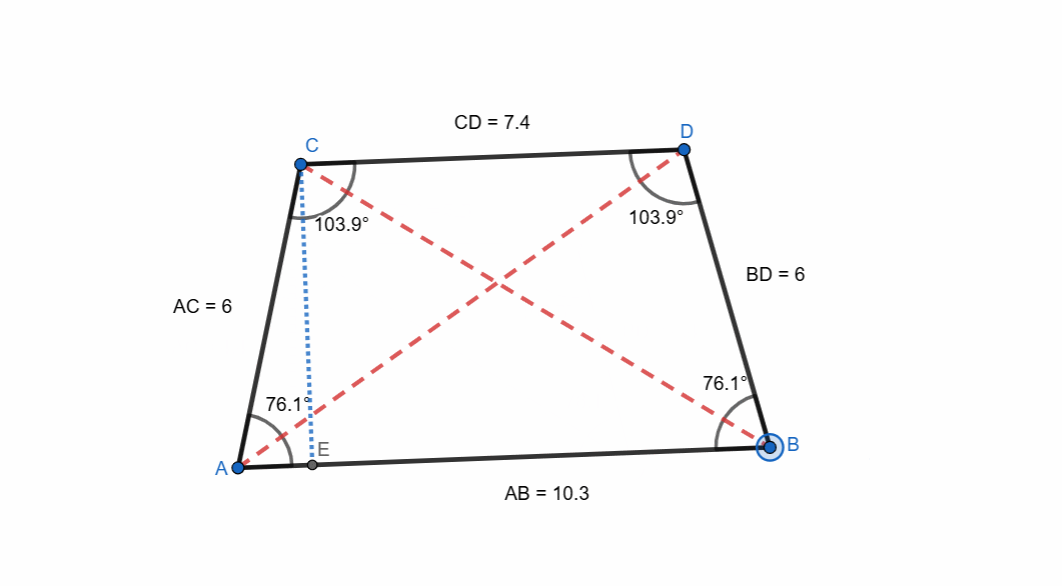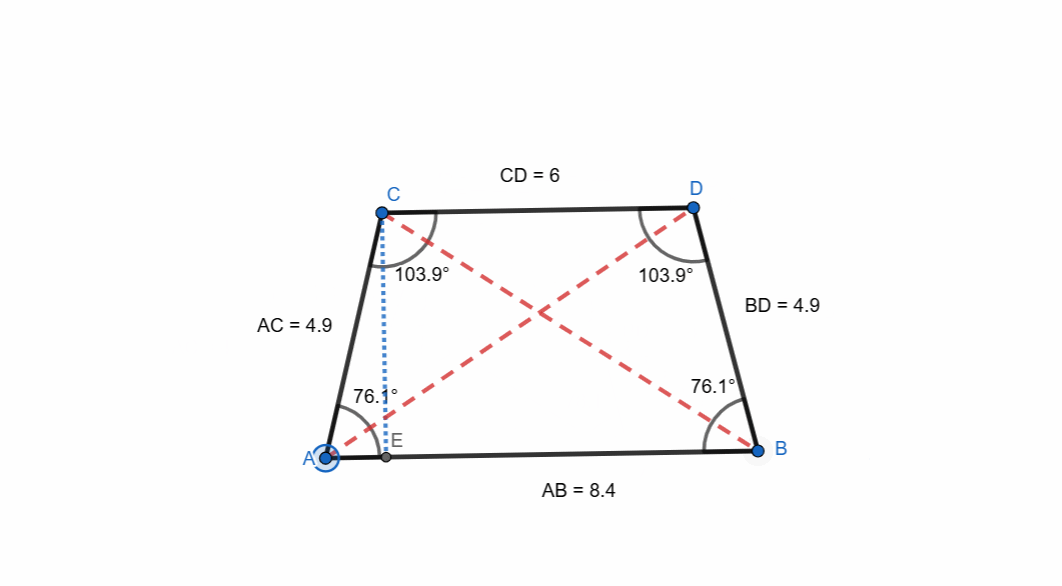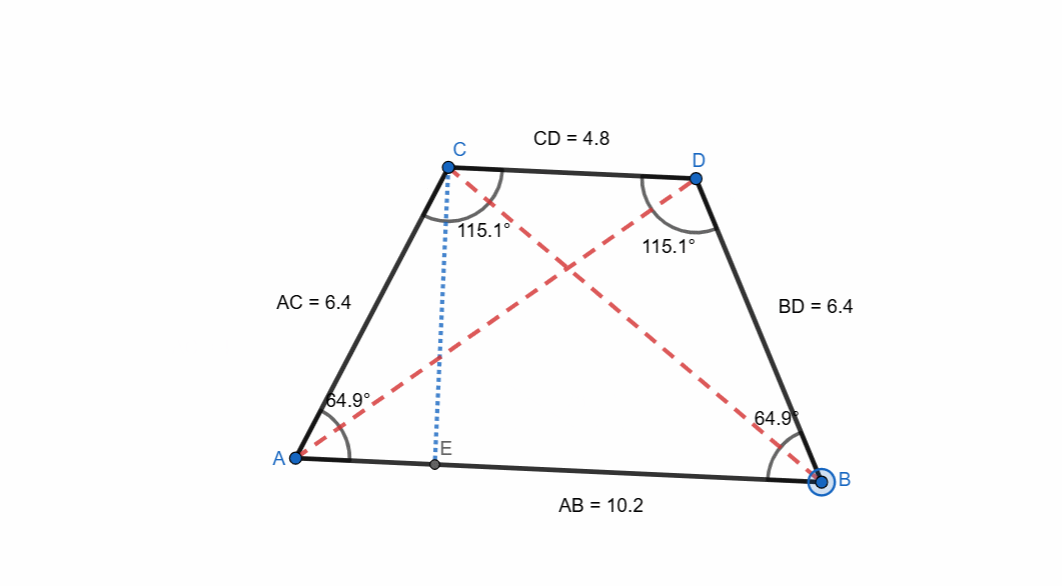
It has following unique properties:
- Equal non-parallel sides.
- Equal base angles.
- Equal diagonals.
- Opposite angles are supplementary.
- It has vertical symmetry.
Build a rhombus, demonstrate its elements and properties.
A rhombus is a special type of the parallelogram where all sides are equal.
In the geogebra I have built rhombus by using the following procedure:
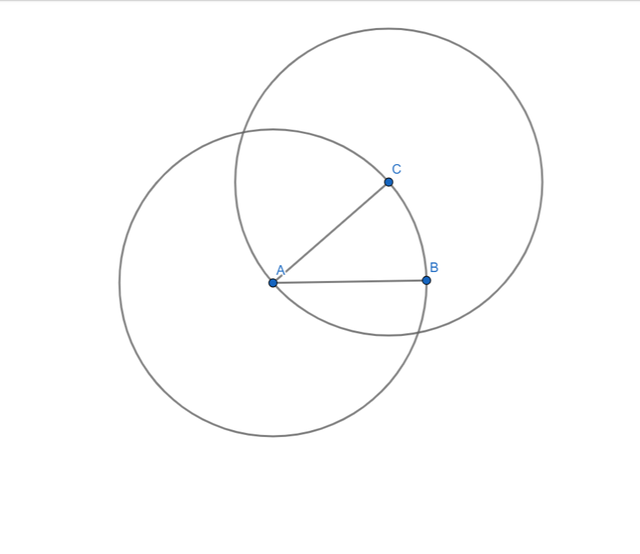
- I took a segment AB.
- I drew a circle at the center A with radius AB.
- I took a third vertex as point C on the circle.
- I connected the point C to A.
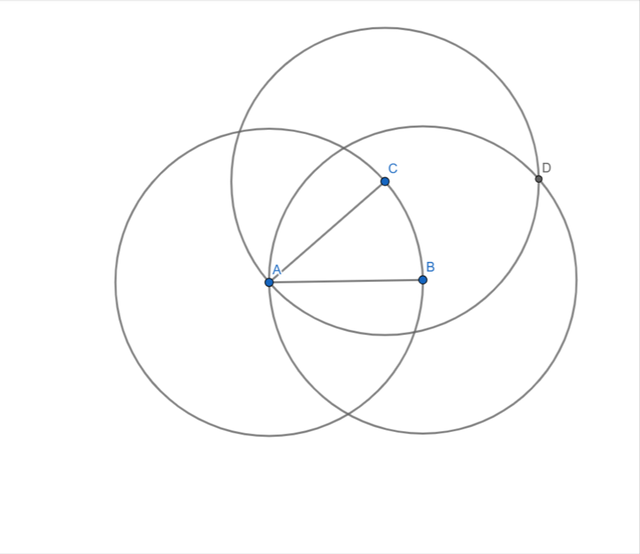
- I formed a circle with center at B with radius AB and similarly at point C with radius AC.
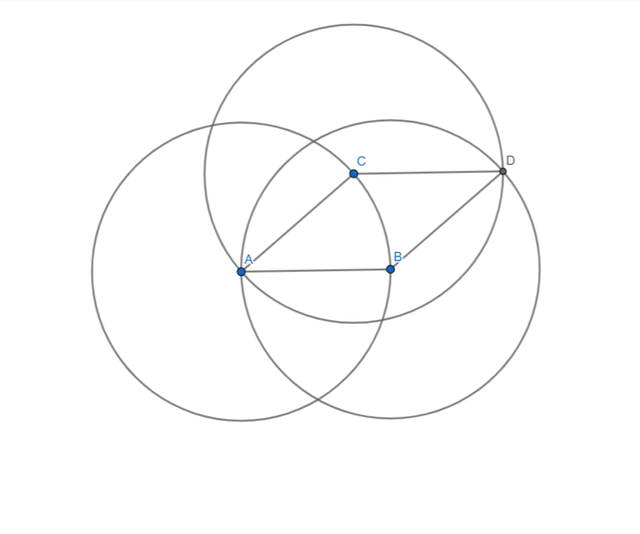
- Their intersection gave me the fourth vertex D.
- I connected D with C and B.
- A rhombus formed.
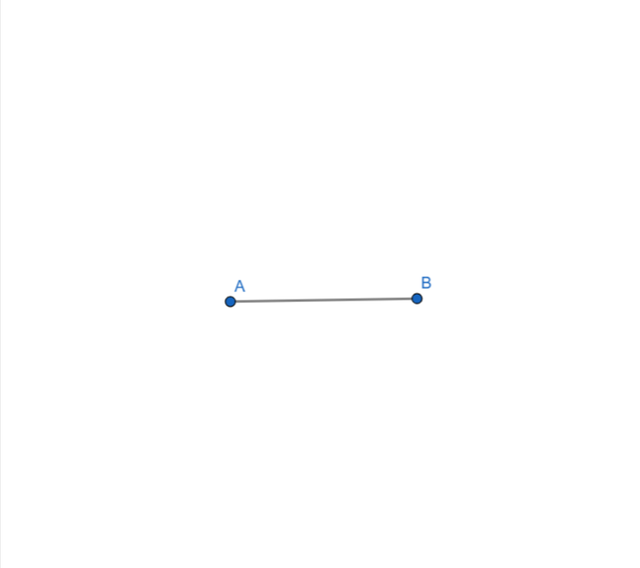 | 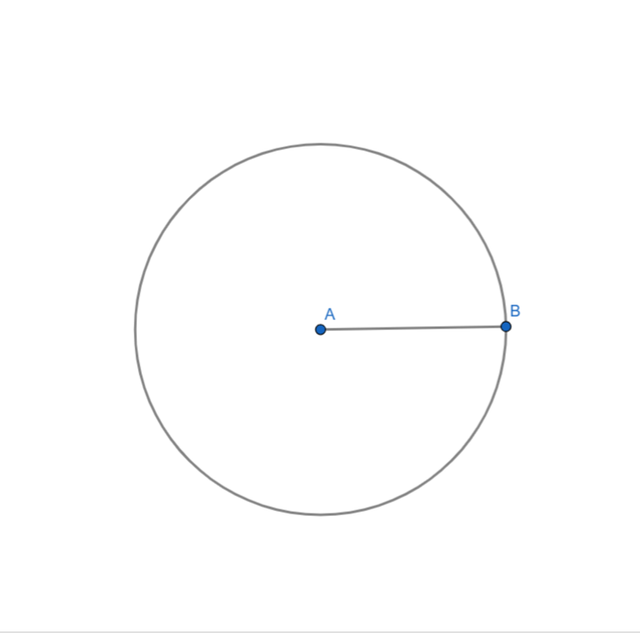 | 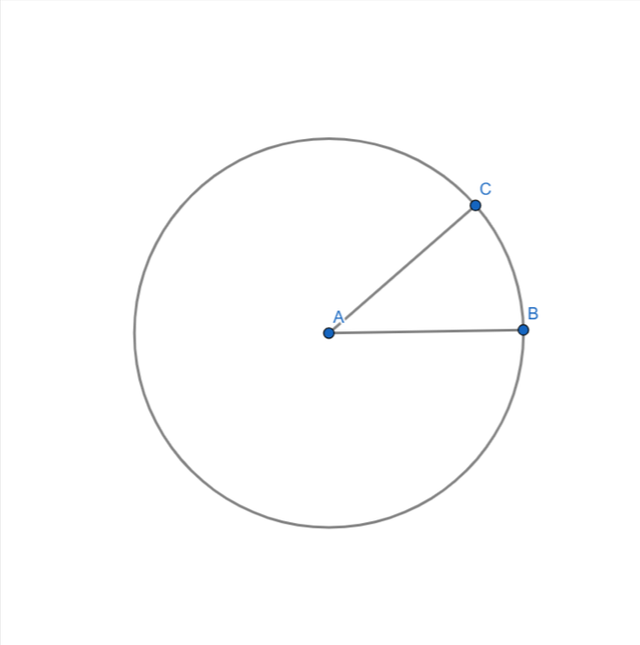 |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 |
 |  |  |
| Step 4 | Step 5 | Step 6 |
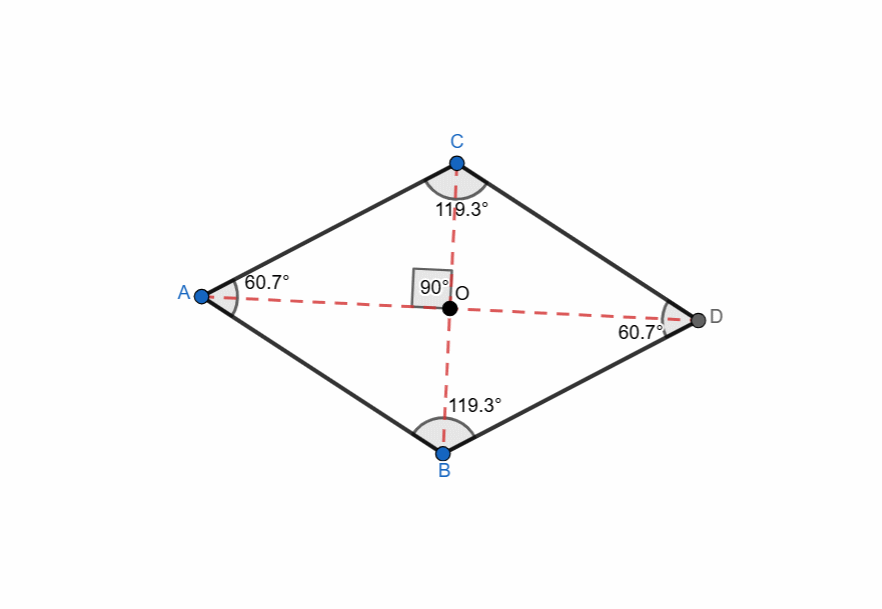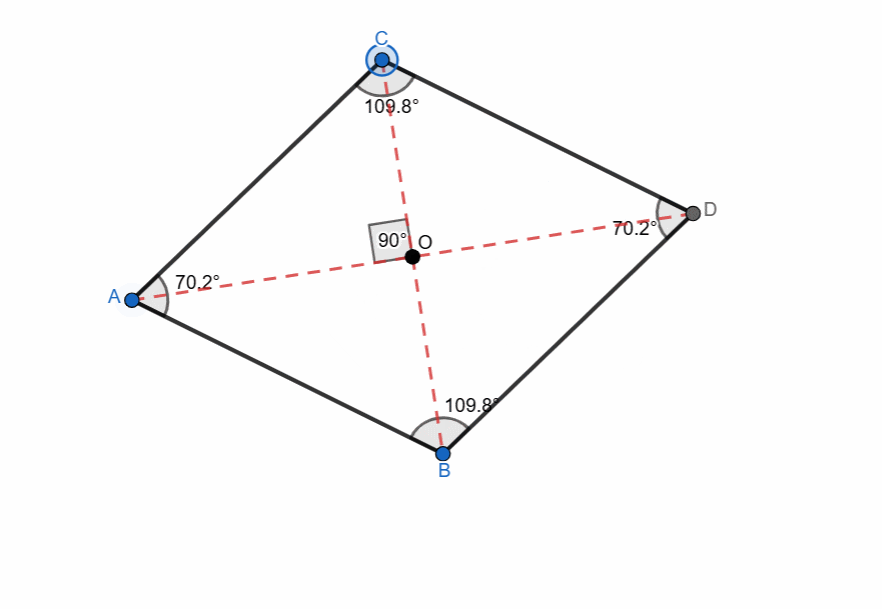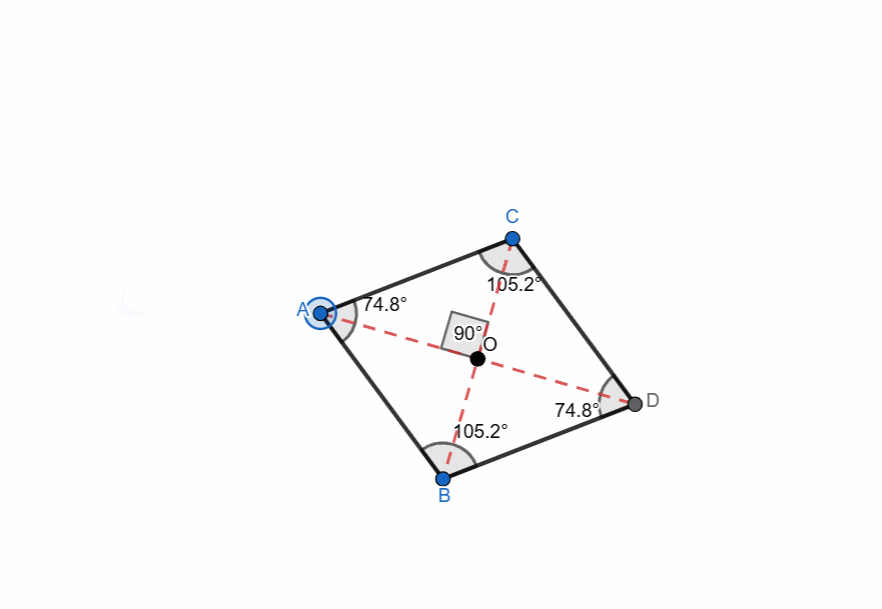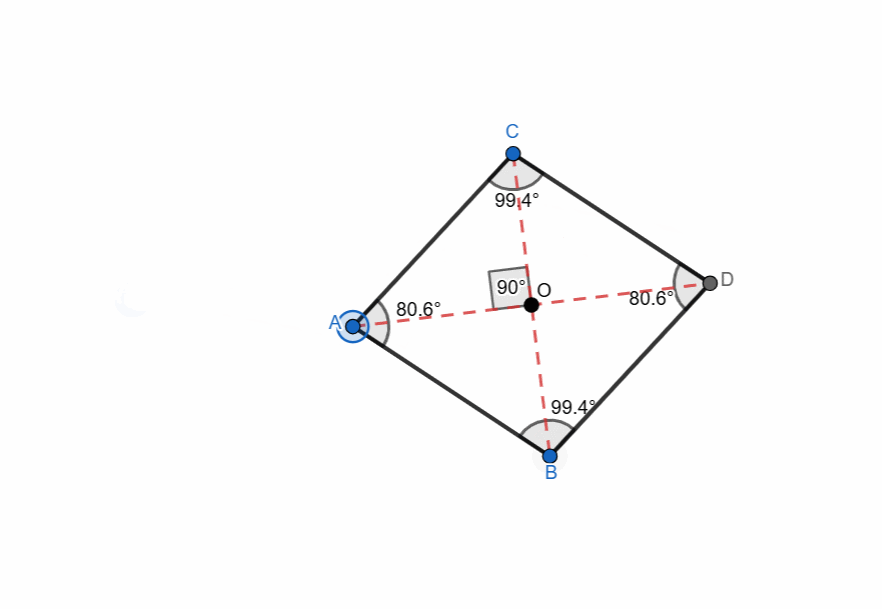
Elements and Properties of Rhombus
Here are all the elements and properties of the rhombus:
- It has four vertices.
- It has four sides.
- The sides are equal in length.
- Two pairs of opposite parallel sides. AB || CD and BD || CA
- There are four interior angles.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- Adjacent angles are supplementary.
- Sum of all the angles is 360.
- The diagonals of rhombus bisect each other at right angle.
- The diagonals bisect the angles of the rhombus.
- One diagonal is major (longer) and the other is minor (shorter).
- The point where the diagonals intersect each other is centroid.
- The perpendicular distance between two opposite sides is the height of the rhombus.
- The area can be calculated from two formulas:
- Area using Diagonals = 1/2 x d1 x d2
- Area using base and height = base x height
- Perimeter of rhombus = 4 x side

Here I have tried to show all the properties of the rhombus and it can be seen that as the shape is changing itself the values are also changing. The adjacent angles are supplementary and the sum of all angles is 360. The diagonals are bisecting each other at right angle all the time. The opposite sides are parallel to each other.
Build a rectangle, demonstrate its elements and properties.
A rectangle is a quadrilateral with all the opposite sides equal in length. All angles are equal to 90.
In the geogebra I have built rectangle by using the following procedure:
- I took a segment AB.
- I used a perpendicular line tool to draw a vertical line from point A.
- I marked the point C randomly on the vertical line.
- I drew a parallel line to AB passing through the point C.
- I used a perpendicular line tool to draw a vertical line from point B. This line intersected the previous parallel line at point D.
- I connected all the points with segments and hide the parallel and perpendicular lines.

Elements and Properties of Rectangle
Here are all the elements and properties of the rectangle:
- It has four vertices.
- It has four sides.
- The opposite sides are equal in length.
- It has four right angles.
- Sum of all the angles is 360.
- Two pairs of parallel sides. Opposite sides are parallel.
- It has two diagonals.
- The diagonals are equal in length.
- Diagonals bisect each other.
- Diagonals bisect the angles.
- The intersection of diagonals is centroid.
- The mid points of both the diagonals is at centroid.
- Area of rectangle = length x width
- Perimeter of rectangle = 2 (length x width)
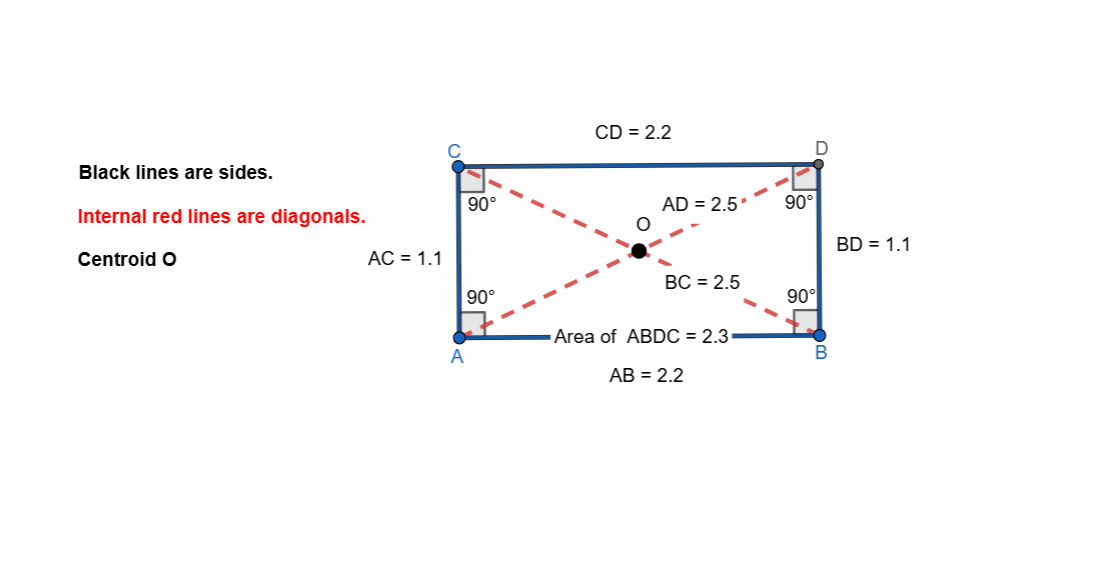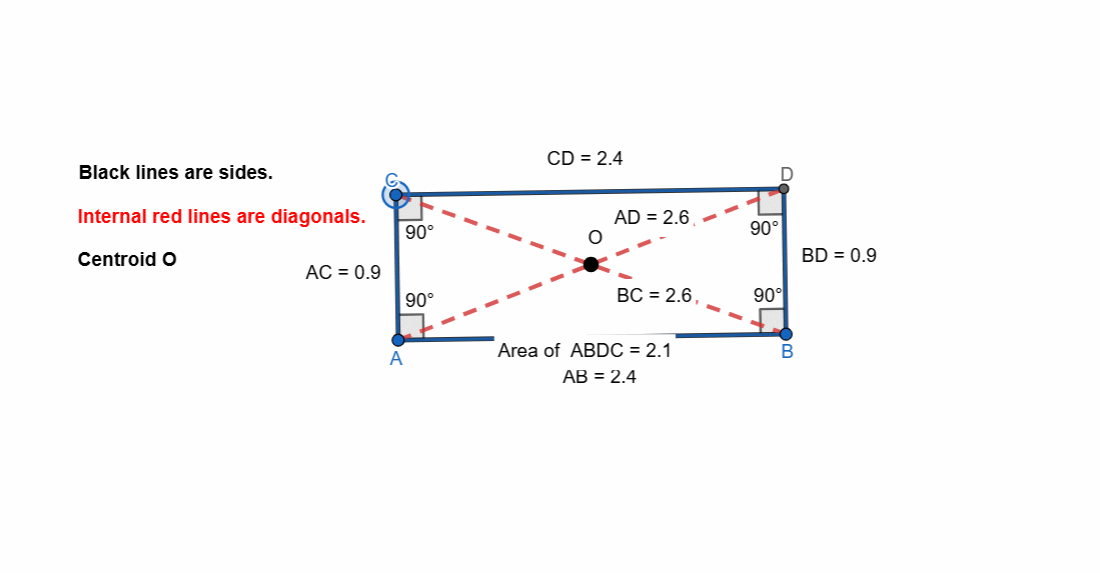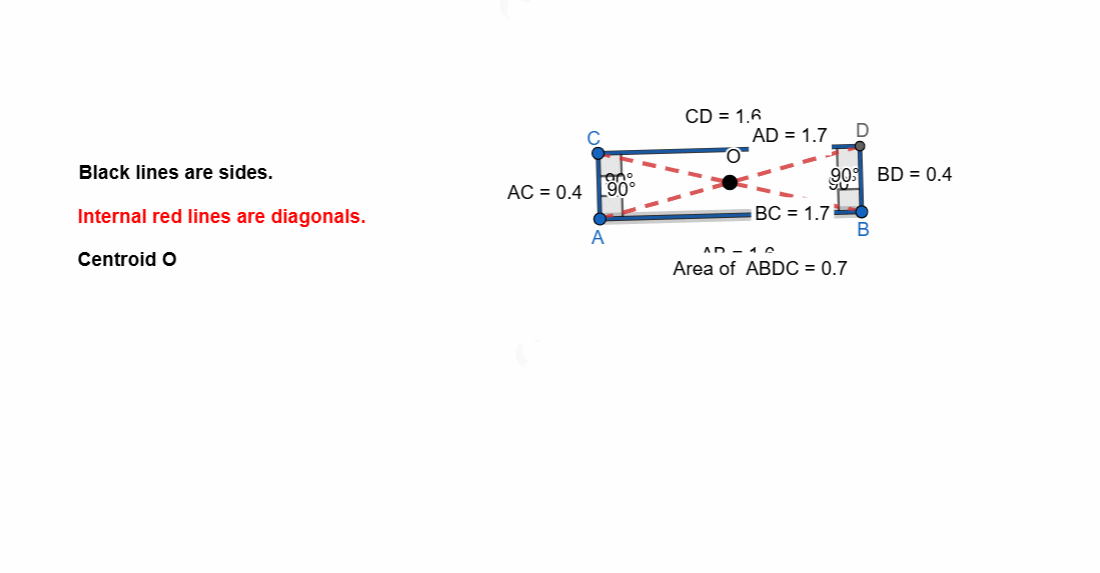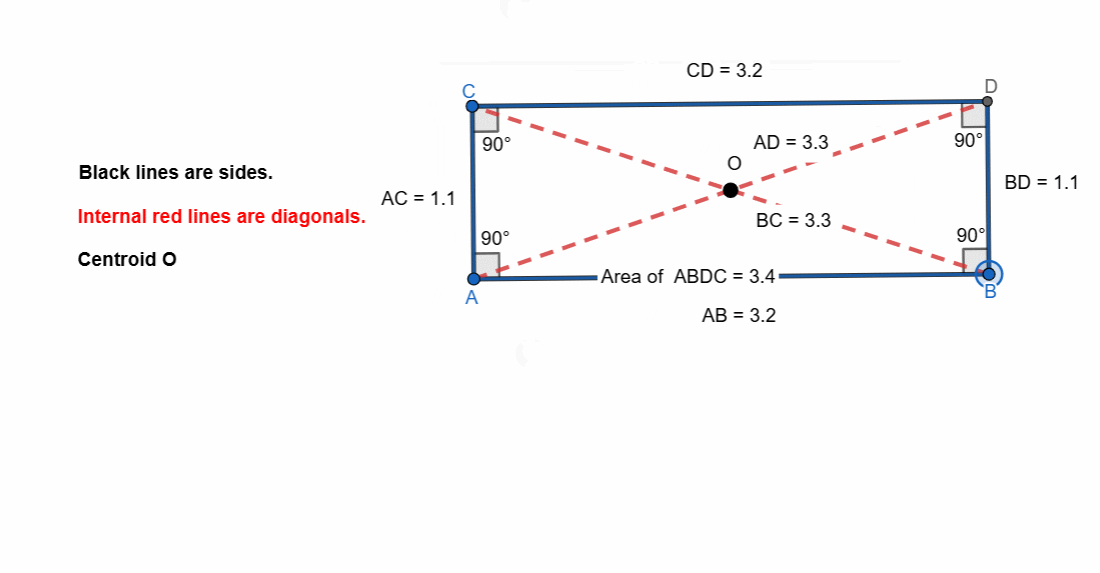
Here I have tried to show all the properties of the rectangle. Opposite sides are equal and parallel. All the angles are right angle. The diagonals are bisect each other.
Build a square, demonstrate its elements and properties.
A square is a special type of quadrilateral where all sides are equal and all angles are 90°. It is also a rectangle and a rhombus at the same time because a rectangle has four right angles and a rhombus has four equal sides and a square has both.
In the geogebra I have built square by using the following procedure:
- I took a segment AB.
- By using perpendicular line tool I drew a vertical line passing through point A.
- I used circle tool to draw the circle centered at A with radius AB.
- This circle intersected the perpendicular line at a point C.
- I drew a parallel line to segment AB passing through the point C.
- Then I drew a perpendicular at point B.
- The parallel and perpendicular lines intersected at point D.
- I connected all the points with segment and hide the other lines and circle.
- The square is formed.
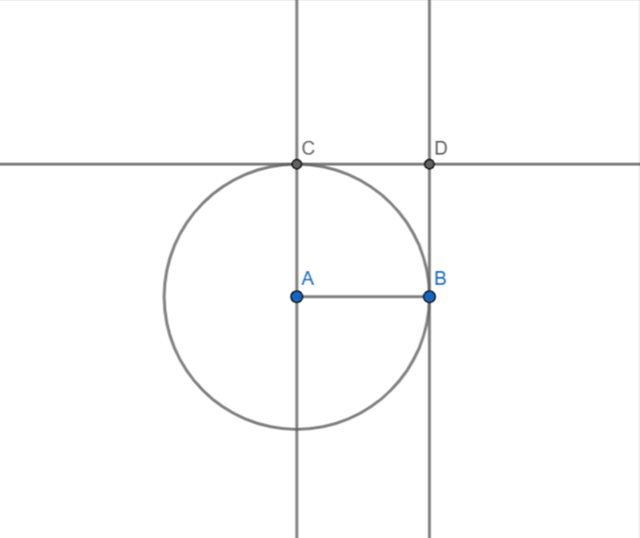 |  |
|---|
Elements and Properties of Rectangle
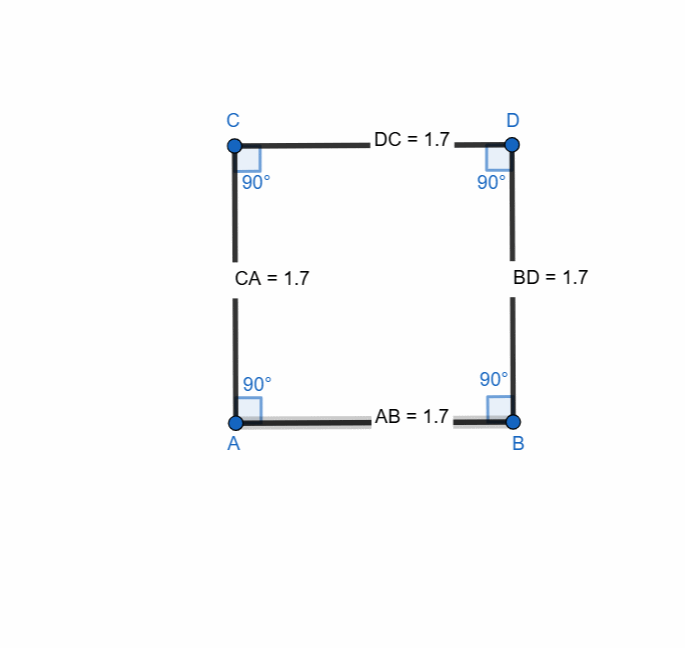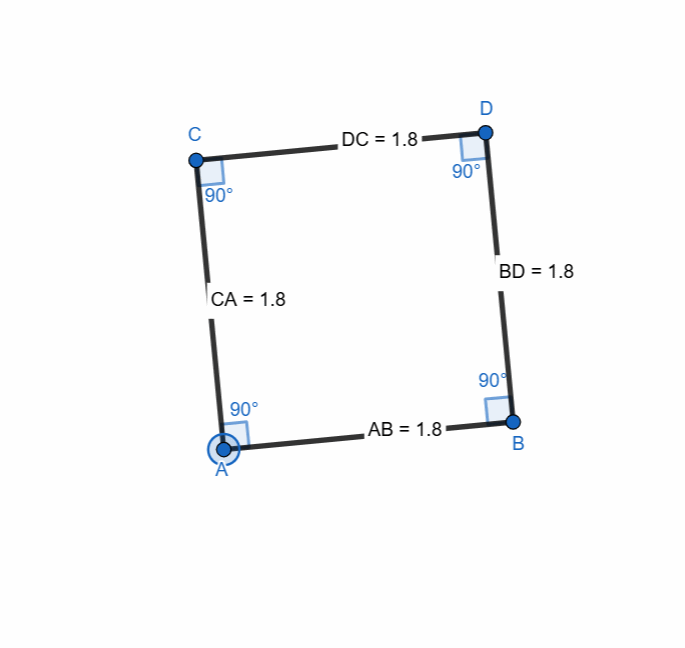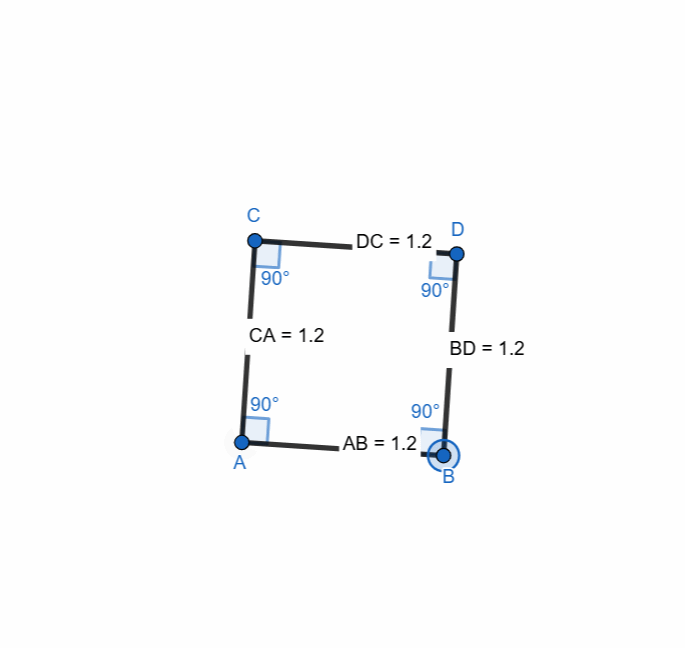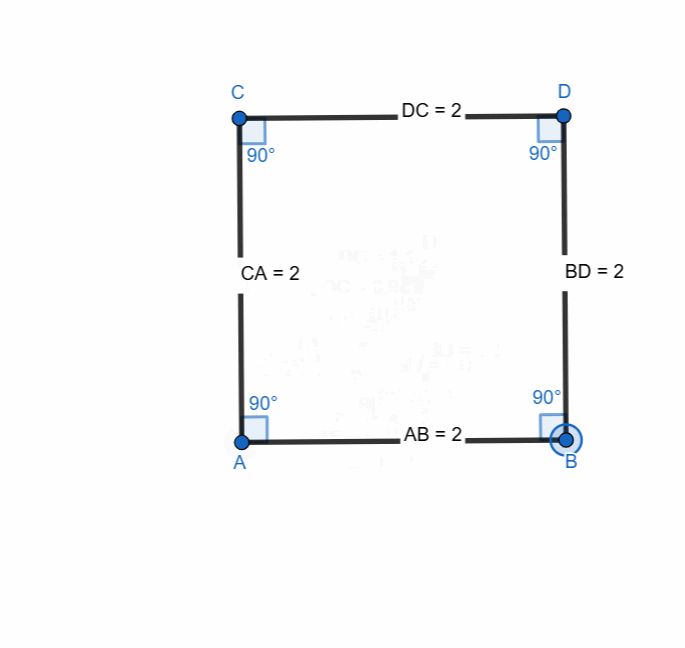
Here are all the elements and properties of the square:
- It has four vertices.
- It has four sides.
- The sides are equal in length.
- It has four right angles.
- Sum of all the angles is 360.
- Opposite sides are parallel.
- It has two diagonals.
- The diagonals are equal in length.
- Diagonals bisect each other at 90 degree
- Diagonals bisect the angles.
- The intersection of diagonals is centroid of center of the square.
- The mid points of both the diagonals is at centroid.
- Area of square = side x side
- Perimeter of rectangle = 4 (side)
- Diagonal length of the square = side√2
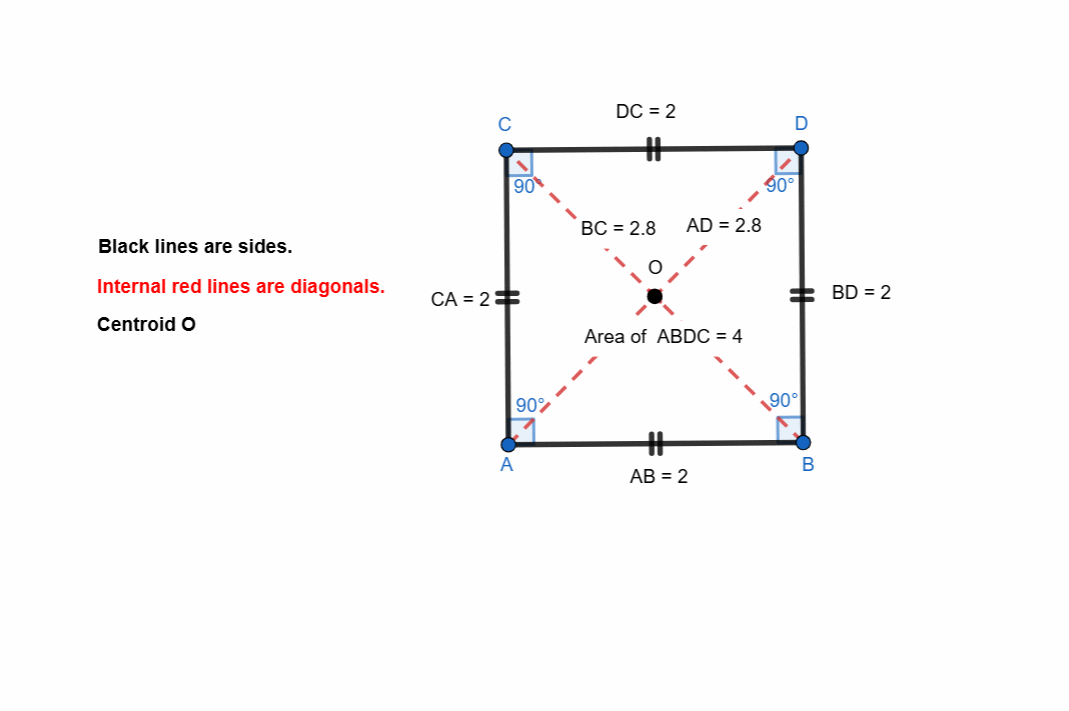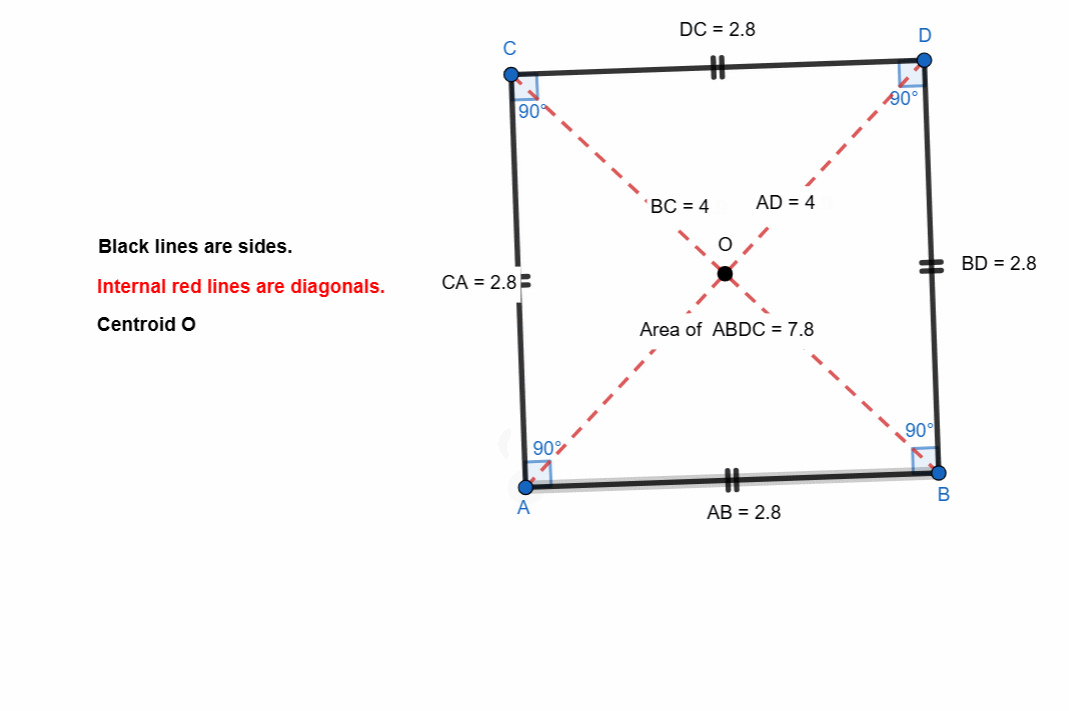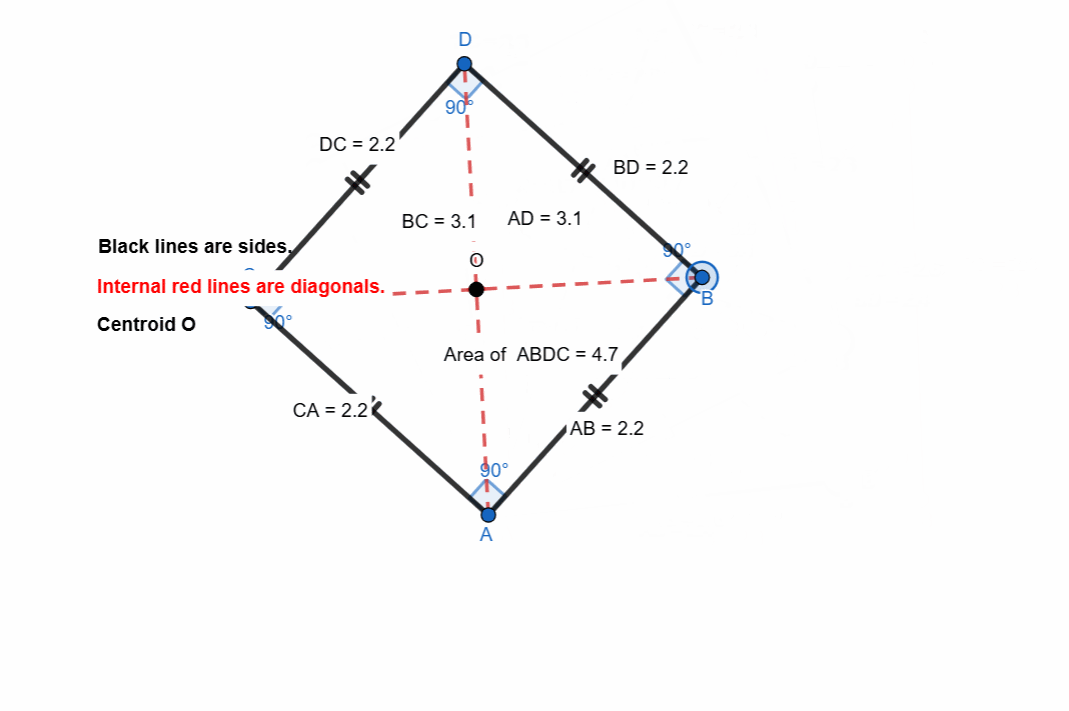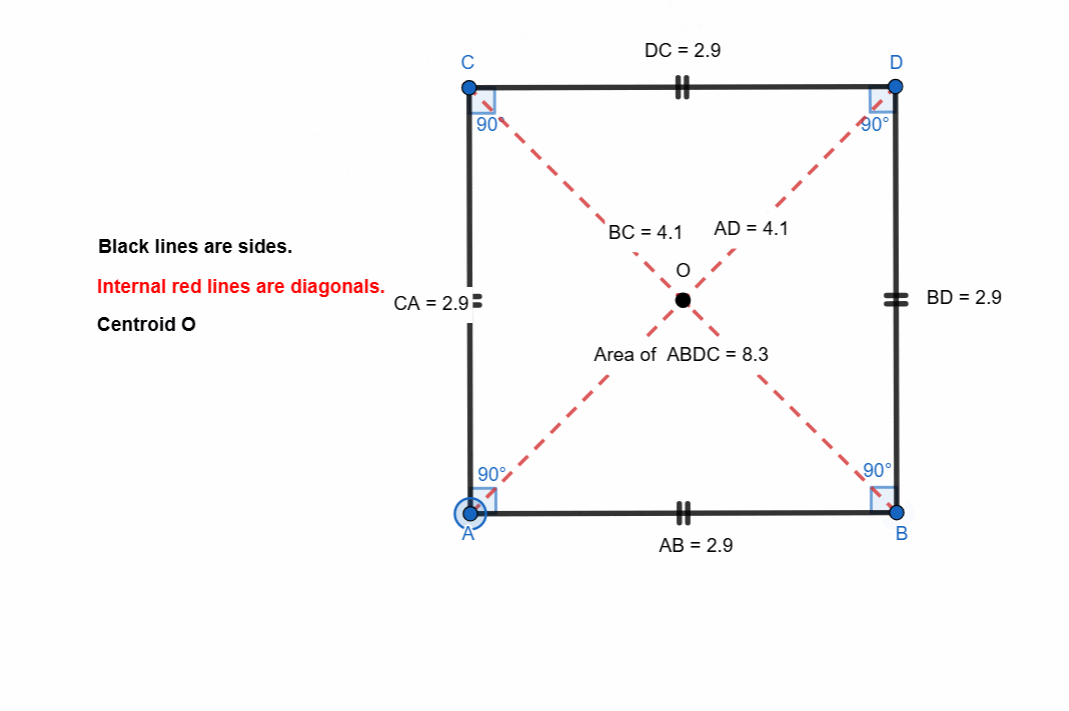
Here I have tried to show all the properties of the square. Opposite sides are equal and parallel. All the angles are right angle. The diagonals bisect each other at midpoints.