SLC S23 Week6 || Computer Repair - HDD & SSD Storage

| Theoretical Questions |
|---|
1️⃣ HDD Structure and Operation:
Question: Describe how an HDD stores and retrieves data. What are the key components inside an HDD?
A computer hard disk is like a miniature turntable enclosed in an air-tight housing. My grandfather had a turntable, but I don't know where my father kept it.
From the motherboard, data in a digital electronic form is sent to the hard disk through a data cable to the electronic circuit on the hard disk. The data is prepared and passed through an arm which has a read/write head that converts the digital data into a magnetic form and is ready to transfer it to the platter. Imagine the read/write head as the needle on the arm in the turntable.
The hard disk platter is like the record on the turntable. The platter(s) is the main storage medium that holds data magnetically. The digital data in the form of zero and one are converted to their magnetic equivalent by the read/write head and its close proximity to the platter results in the induction of a similar orientation on the platter which is made up of a ceramic material-coated with a magnetic coating and divided into sectors on a track that forms a concentric circle.
For data to be retrieved, the same process takes place in the reverse order, exactly the way a turntable reads music out of a record.
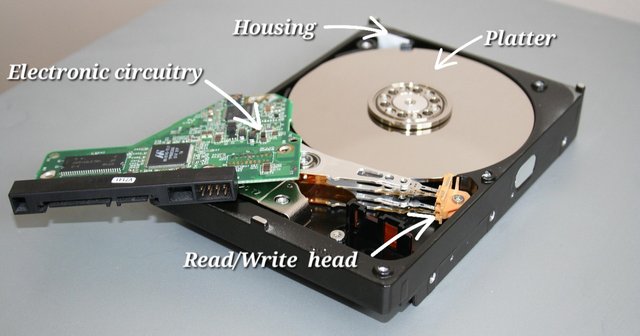
The key components here are:
 My hard disk is still operational, and due to its delicate nature, I did not open it so I got this picture from pixabay.com for better illustration.
My hard disk is still operational, and due to its delicate nature, I did not open it so I got this picture from pixabay.com for better illustration.
Besides the hard disk housing, some bearings, flexible cables, dampers and data controllers the main components are:
Platter
The platter can be a single platter or a stack of shining platters made of ceramics to avoid expensively and coated with aluminium oxide to give it its magnetic properties and formatted into microscopic concentric tracks and sectors with a special track called track zero.
Main spindle
This is a spinning motor that spins the platter at a speed of 5400 RPM, so fast that a cushion of air is created on its surface that helps the read/write head glide on it without any friction.
Read/write head
The read-and-write head is a transducer with a special coil that converts electrical signals into their magnetic equivalent when saving data to the platter and from magnetic to electrical signals when reading from the platter.
The Actuator arm
This is an arm that is controlled by a magnetic coil, it carries the read/write head at one end, hovering it above the platter and moving it to a position where it can read or write onto the platter. The other end of the actuator has a flexible wire that transmits the signal to or from the circuitry.
Electronic circuitry
The electrical circuitry is a board that carries different chips responsible for controlling the spindle, the movement and positioning of the actuator arms, the conversion of digital pulses into electronic signals and the reverse. It also carries the software and physical interface between the hard disk and the motherboard.
2️⃣ SSD Advantages:
Question: What makes SSDs more efficient and reliable than HDDs? In what scenarios is it preferable to use an SSD?
Vibration
A solid-state drive does not have platters that spin at high speed, nor does it have a read/write head. Without any moving parts, it means a device with a solid-state drive will experience no drive vibrations.
Access speed
The seek time for accessing data will be relatively shorter, making it faster when saving and retrieving saved information.
Damage
We can rule out any mechanical damage from the SSD because it has no mechanical parts. No broken read/write head or drive with an irritating, squishy, or grinding sound.
Light weight
Most of the weight of the hard disk is due to the mechanical parts and their supporting frames. With the absence of moving parts, the solid-state drive is much lighter.
When SSD is preferable
You will really need a solid-state drive for a device that is often on the move. Advisable for recording data captured by a moving car, a flying drone that makes acrobatic manoeuvres.
Due to its lightweight, it is recommended for devices that should be lightweight, wearable devices or devices that will be carried by a small drone or a small atom notebook PC.
A lack of mechanical parts means no need for servicing, and as such, a solid-state drive will do better for very long-term storage. Keeping a traditional hard disk without using it can disappointment after being idle for a long time.
3️⃣ Internal vs External Drives:
Question: What are the pros and cons of using an external hard drive compared to an internal one?

Portability
Internal drives are made to be kept stationary, good for desktop computers, while external drives are to be carried from place to place.
Flexibility
You can use an external drive at home and at the office while a fixed disk will only stay at the office.
It can be used on a desktop, laptop, TV and other devices.
Security
The internal drive at the office is always in the computer and can be stolen because its location is always known, while an external drive will be disconnected after use and relocated to an unknown place.
Access speed
Internal drives have higher speed while the USB makes external drives slower compared to the internal drive.
Durebility
The system's housing and the stationary nature of the internal drive protect it against mechanical damage, while external drives are easily damaged if they fall down.
Cost
Getting a 500Gb drive for internal storage is less expensive when compared to a 500Gb external drive because you will also have to buy an external drive enclosure to put it, and it may require external power.
Virus
As it goes from computer to computer, the external drive is often the one that gets and spreads computer viruses. That is why I always scanned my external drive for malicious software.
Pros and cons of external and internal drives
| Particulars | Internal | External |
|---|---|---|
| Portability | not portable | very portable |
| Flexibility | use on one device | use on many devices |
| Security | less secured | more secured |
| Misplace | can not get lost | can get lost |
| Durability | longer life | shorter life |
| Cost | cheap | expensive |
| Practical Tasks |
|---|
4️⃣ Task: Inspecting Your Drive Type and Connection
- Question: Open your PC/laptop (if possible) and take a photo of your internal or external drive. Identify if it’s an HDD or SSD and mention its size and type (SATA, NVMe, etc.).*
The video below shows how to access and identify a drive type and capacity. I was using an HP Elitebook laptop for the exercise.
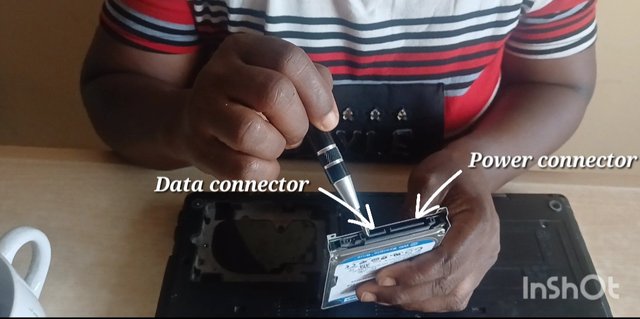
Showing in the picture below, the capacity of this internal drive is 160Gb. It was a big drive in the past, but going by today's standards, a 160 GB drive is relatively small.
The drive capacity or size determines the amount of data/information that can be stored on the drive. If your plan is to store large volumes of data, you will need a drive that has its capacity in terabytes.


The housing, spindle and structure show that this drive is a traditional hard disk drive and not a solid-state drive.
I am inviting @josepha, @bela90, @okere-blessing and @ruthjoe to participate in this contest.
Engineer udyliciouz I commend your seriousness throughout this learning challenge. I have watched you countless times showcasing what you are good at without charging us. I wish I can learn repairs . You are good and I wish you good luck in this challenge.